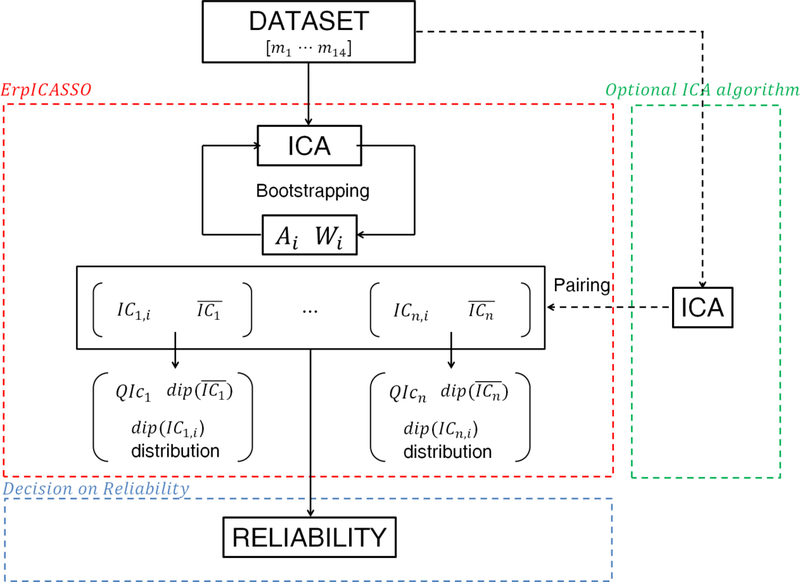
Figure 1.
A schematic of the RELICA method to test the reliability of independent component (IC) processes separated from EEG data sets. The data set is first decomposed using an ErpICASSO approach (red box); for each resulting IC cluster a reliability decision is made (blue box). Within ErpICASSO, the ICA decomposition is performed n times, each time yielding a matrix Ai and Wi. ICs are clustered according to their similarities, and one IC is extracted from each cluster. Then the IC dipolarity, , QIc and dip(ICn,i) distributions are computed. Based on those values, it is possible to decide on the reliability of a component. For multi-subject experiments, it is possible to add measures of between-subject stability of components as in the ICA data analysis approach now embodied in EEGLAB. (The green box and dotted line represent an optional step that could be added to RELICA, as explained in the Discussion).