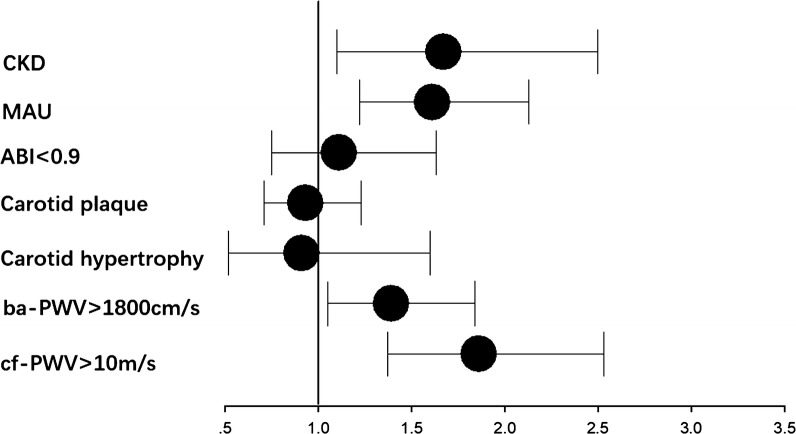
Fig. 2.
Q4 (fourth quartile) vs Ql (first quartile) odds ratio(OR) of TyG index for macro-and microvascular damage after adjustment for age, sex, BMI, WC, smoking habit, hypertension, family history of premature CVD, diabetes, HDL-C, LDL-C, insulin therapy and statin therapy. TyG index levels for Q4 was associated with increased OR for cf-PWV > 10 m/s, ba-PWV > 1800 cm/s, MAU and CKD, but not for ABl < 0.9, carotid hypertrophy or carotid plaque in multivariable logistic regression. TyG triglyceride glucose, cf-PWV carotid-femoral pulse wave velocity, ba-PWV brachial–ankle pulse wave velocity, ABI ankle–brachial index, MAU microalbuminuria, CKD chronic kidney disease, BMI body mass index, WC waist circumference, CVD cardiovascular disease, HDL-C high-density lipoprotein cholesterol, LDL-C low-density lipoprotein cholesterol