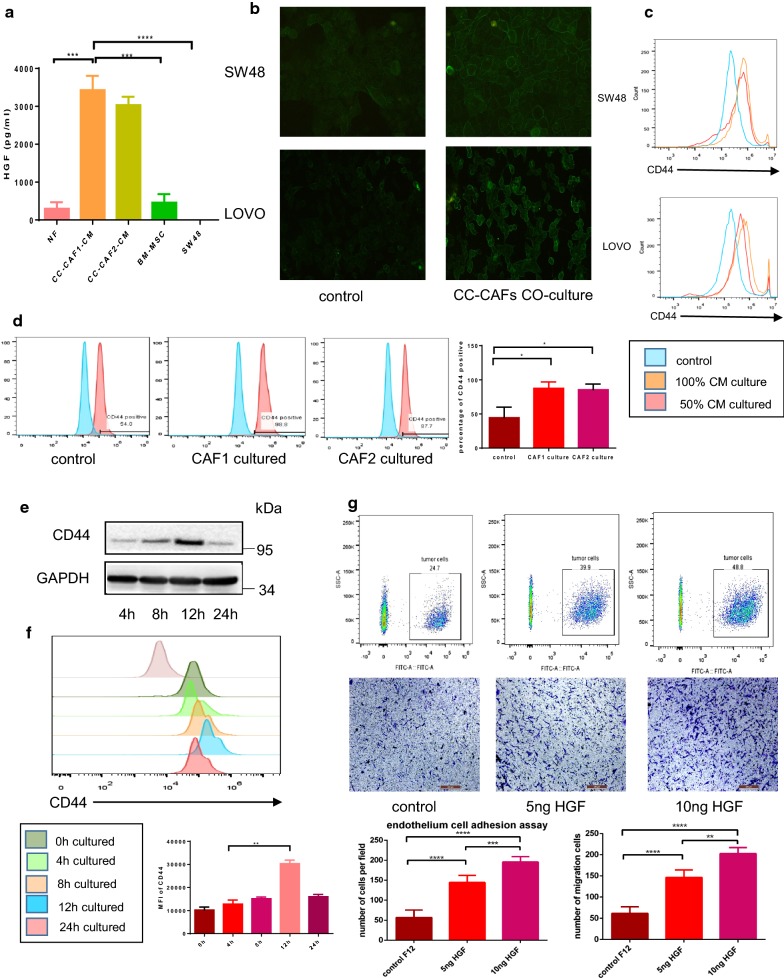
Fig. 3.
CC-CAFs-derived HGF maintained adhesion and migration capacity of CRC cells through up-regulation of CD44. a Quantitative analysis of HGF by using enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). The condition medium of NFs, SW48, BM-MSC and CC-CAFs were collected to detect level of HGF. The CC-CAFs were isolated from two patients (n = 3). Error bars represent mean ± s.d; ***P < 0.001; ****P < 0.0001. b Expression of CD44 in SW48 and LOVO cells with or without CC-CAFs-CM treatment was detected by immunofluorescence (magnification, ×200). c SW48 cells were cultured with different dilution ratio of CC-CAFs-CM for 12 h. CD44 expression was determined by flow cytometry in SW48 (top) and LOVO (bottom). d Expression of CD44 in SW48 co-cultured with or without 2 CAFs was evaluated by flow-cytometry, *P < 0.05. e SW48 cells were cultured with CC-CAFs-CM for different times. Protein expression was analyzed by western-blot. f SW48 cells were cultured with 5 ng/ml HGF for different times. CD44 expression was determined by flow cytometry. **P < 0.01. g Adhesion assay (top) and transwell migration assay (bottom) of SW48 cells subjected to different HGF concentration (magnification, ×100; scale bar: 250 μm). Error bars represent mean ± s.d; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001; ****P < 0.0001; by one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA)