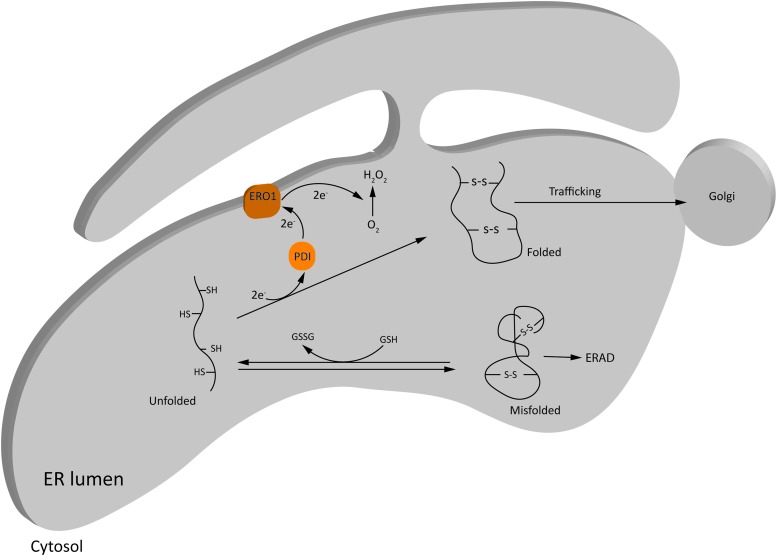
FIG. 3.
Basal ROS production in ER during oxidative protein folding. Oxidative protein folding in ER is one of the major contributors of ROS in the cell under physiological conditions. Disulfide bond formation in the nascent proteins is achieved through exchange of electrons between the cysteine residues of the substrate protein and the ER oxidoreductases, PDI and ERO1, and finally transferred to molecular O2, resulting in the production of H2O2. Misfolded proteins can be refolded at the expense of GSH, or get degraded via ERAD. See the Basal ROS production in ER and ER stress section for details. ER, endoplasmic reticulum; ERAD, ER-associated protein degradation; ERO1, ER oxidoreductase 1; GSH, reduced glutathione; GSSH, oxidized glutathione; PDI, protein disulfide isomerases. Color images are available online.