Figure 2.
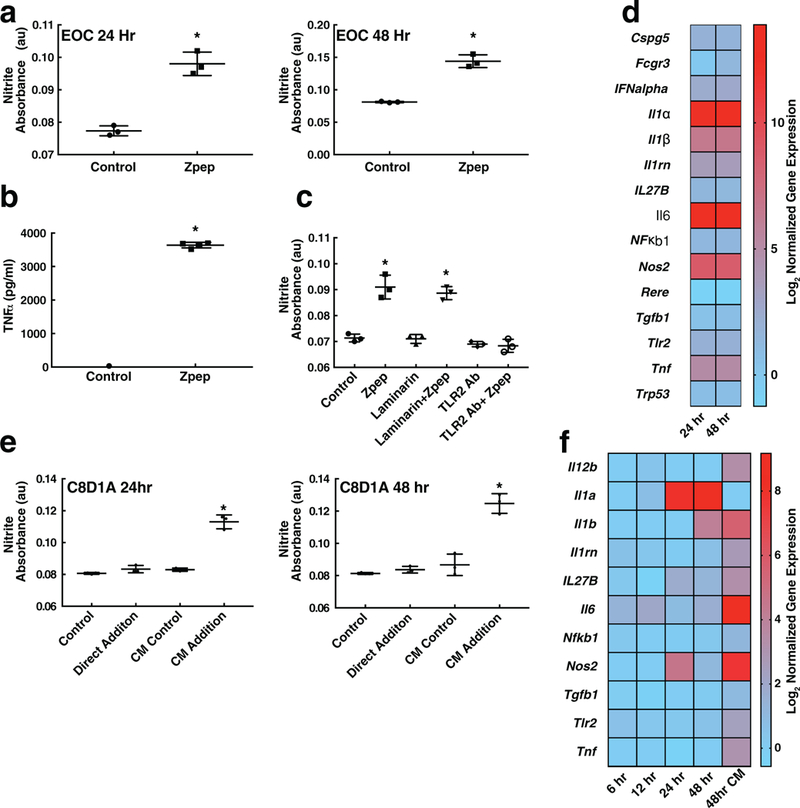
Zymosan peptide (Zpep) causes glial cell activation. Addition of Zpep to EOC mouse microglial cell line causes increased nitric oxide production over time, as assessed by a) the Griess assay and b) the secretion of TNF-α. c) Zpep activates glial cells via toll-like receptor 2 (TLR2). EOC cells were treated with laminarin (to block dectin-mediated recognition) or TLR2-blocking antibody prior to exposure to Zpep. Only TLR2 blocking led to a decrease in nitric oxide production by EOC cells, indicating that Zpep retains the TLR2 activating properties of zymosan. d) Zpep addition led to the upregulation of inflammatory gene transcripts. e) EOC-conditioned medium, but not direct addition of Zpep, activates astrocytes. CM indicates EOC-conditioned medium. Direct addition of Zpep to C8D1A astrocytes failed to induce nitric oxide production even after 48 h of exposure. Conversely, addition of EOC-CM to C8D1A cells induced e) nitrite production and f) upregulated inflammatory gene transcripts at both 24 and 48 h. *p < 0.05; Student’s t-test in a and one-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s test in (c), (e), and (f). Data are plotted mean ± standard deviation.
