Figure 2.
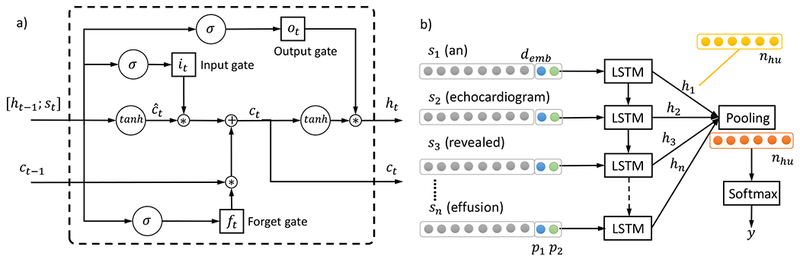
Illustration of LSTM model. a) The building blocks – LSTM memory cell. The operator “;” denotes vector concatenation, σ(·) and tanh(·) refer to the element-wise sigmoid and hyperbolic tangent functions, and * is the element-wise multiplication. The ft, it, ot are the values of the forget gate, input gate and output gate respectively, ĉt is the candidate value for the cell state, Wf, Wi, Wc, Wo are weight matrices and bf, bi, bc, bo are bias vectors associated with them. b) The sentence level LSTM model architecture for relation classification. Each LSTM block corresponds to the memory cell structure in a). Each input st, t = 1,…,n has a dimension of demb that is the word embedding size, plus two numbers p1, p2 corresponding to the distances of the current word to concept 1 and concept 2 respectively. Each LSTM memory cell output ht has a dimension of nhu, which are then pooled to produce a feature vector of dimension nhu as well. The pooling output can be regarded as the hidden units, which are input to the softmax layer that produces the label y for relation classification.
