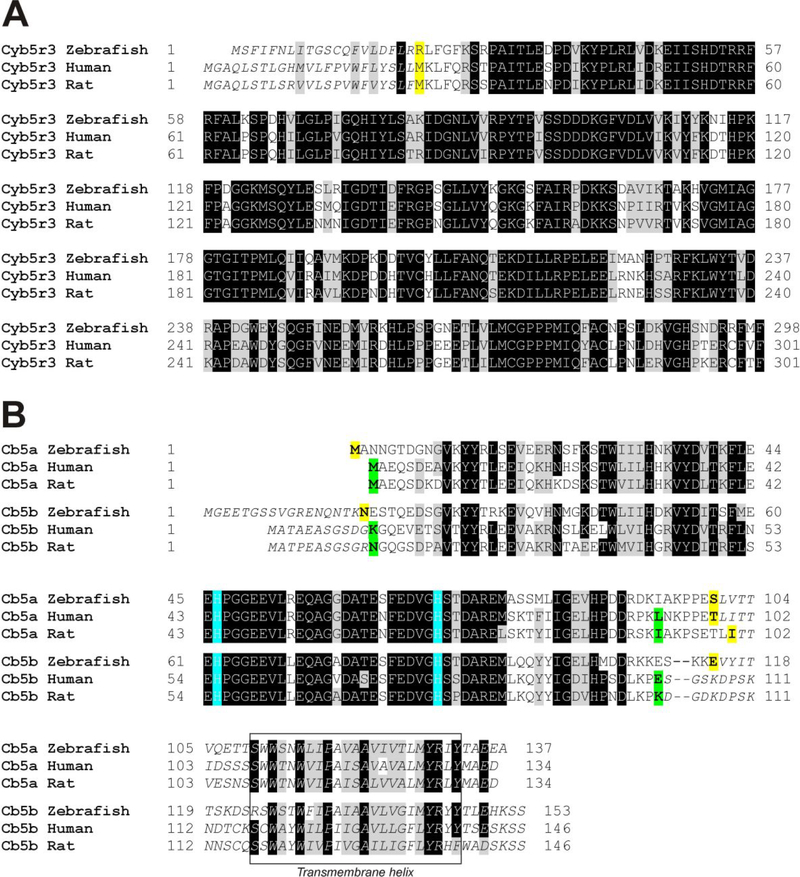
Figure 1. Alignment of cytochrome b5 reductase and cytochromes b5a and b5b protein sequences for zebrafish, human, and rat.
A; alignment of CYB5R3 sequences (Uniprot accession codes: zebrafish, Q6NYE6; human P00387; rat, P20070). Initial portions in italics indicate the missing residues in the soluble isoform (CYB5R3–2) of the mammalian proteins and the homologous residues in zebrafish protein; the first amino acid in the recombinant protein used in this work and the initial amino acid in the mammalian isoform 2 are marked in bold and yellow background. B; alignment of CYB5a (microsomal CYB5) and CYB5b (outer membrane CYB5) sequences (Uniprot accession codes: zebrafish b5a, Q7T341; human b5a, P00167; rat b5a, P00173; zebrafish b5b, Q6NY41; human b5b, O43169; rat b5b, P04166). Conserved heme-binding histidines are indicated in blue background. Amino acids in italics indicate sequences removed in the N-termini of CYB5b and the membrane binding C-terminal regions of CYB5a and CYB5b. The putative membrane intercalating helix region is shown in a rectangle. The first and last amino acids in the recombinant proteins used in this work, along with the splicing sites for the soluble isoform of mammalian cytochrome b5a proteins are marked in bold and yellow background; the first and last amino acids in the recombinant proteins used in other works25, 26 are indicated in bold with green background.