Figure 4. Comparison of the Val59-Trp64 loop in structures of Polη incorporating dCTP opposite the 3′G, Pt(NH3)2−3′G, and Pt(DACH)−3′G.
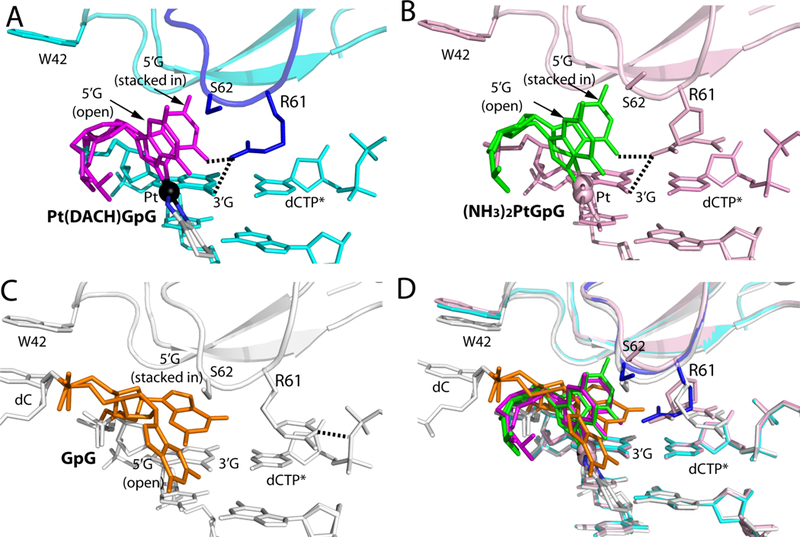
(A) A close-up view showing the Val59-Trp64 loop in the structure of the Polη:Pt(DACH)−3′G:dCTP complex. The 5′G is colored in magenta and its stacked-in and open conformations are indicated. The Val59-Trp64 loop is colored in blue and Pt is shown in a black sphere. Arg61, Ser62, and Trp42 are shown in sticks. Hydrogen bonds between Arg61 and Pt(DACH)GpG are indicated as dotted lines. (B) Structure of Polη incorporating dCTP* opposite Pt(NH3)2-3′G (PDB ID: 4DL4 [39]). Polη and DNA are colored in pink and the 5′G in green. (C) Structure of Polη incorporating dCTP* opposite undamaged 3′G (PDB ID: 4DL2 [39]). The 5′G is colored in orange, whereas protein and DNA are shown in white. Arg61 in the Val59-Trp64 loop engages in a hydrogen bond with a phosphate of dCTP. Note that a stacked-in 5′G is in a syn conformation, whereas an open 5′G is in an anti conformation. (D) Superposition of the Pt(DACH)−3′G, Pt(NH3)2-3′G, and undamaged 3′G structures.
