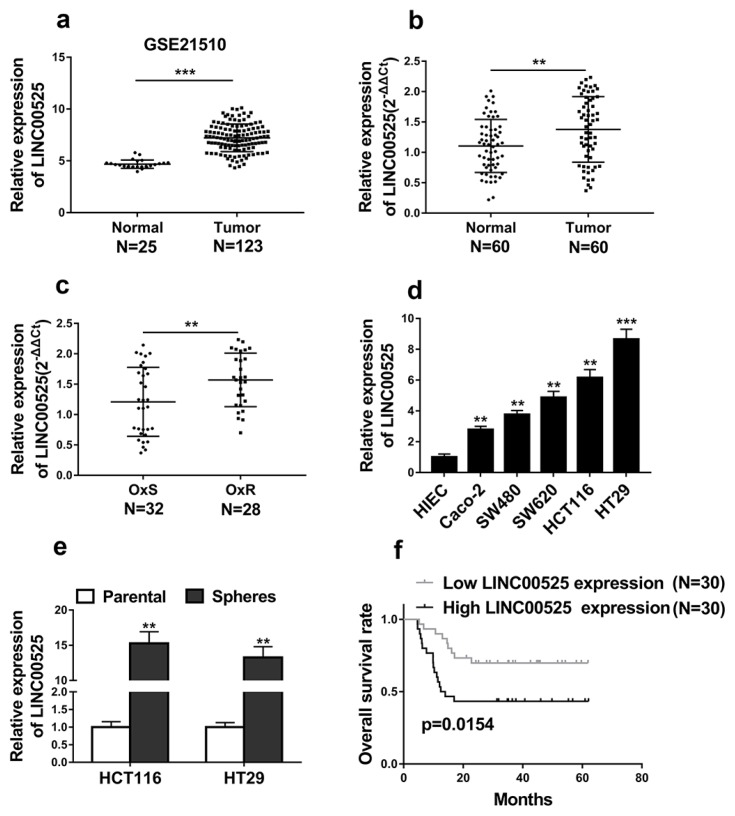
Fig. 1.
LINC00525 was highly expressed in CRC and increased LINC00525 expression predicted poor prognosis in CRC patients. (a) The expression level of LINC00525 was analyzed in CRC tissues compared with normal tissues from GSE21510. (b) qRT-PCR analysis of LINC00525 expression in CRC tissues (n=60) and normal human intestinal tissues (n=60) (shown as log10 (2−ΔΔCT)). (c) The LINC00525 expression level was quantified by qRT-PCR analysis in CRC tissues of oxaliplatin sensitive patients (OxS) and oxaliplatin resistant patients (OxR). (d) qRT-PCR analysis of the relative expressions of LINC00525 in five CRC cell lines (Caco2, SW480, SW620, HCT116, and HT29) and a normal human intestinal epithelial cell line (HIEC). (e) qRT-PCR analysis of the relative expressions of LINC00525 in sphere-forming HCT116 and HT29 compared to parental HCT116 and HT29 cells. (f) Kaplan–Meier’s analysis of the correlation between LINC00525 expression and the overall survival of CRC patients. *p<0.05, **p<0.01, ***p<0.001.