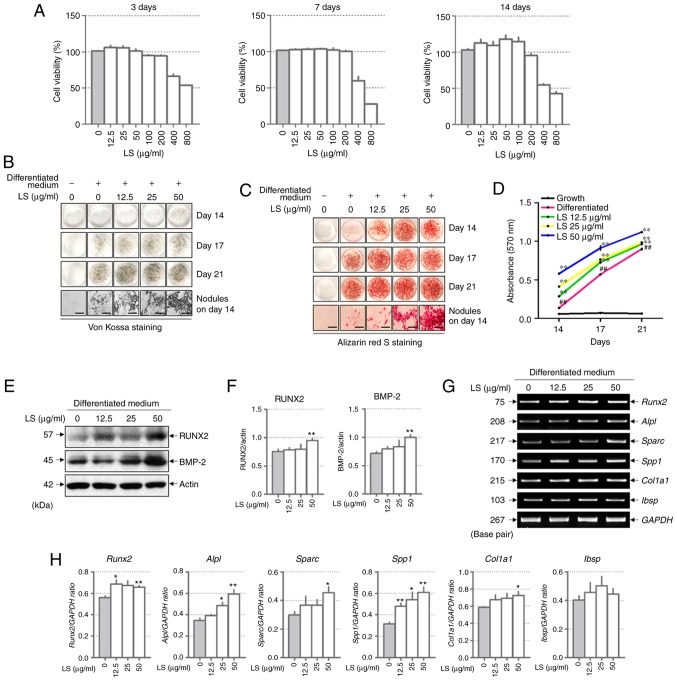
Figure 2.
Effect of LS on osteoblast differentiation. (A) Cytotoxicity of LS used in osteoblast promotion assays was confirmed using an MTS assay for 3, 7 and 14 days. Calcified nodules produced by osteoblasts were stained with (B) Von Kossa and (C) Alizarin Red S (×100 magnification; scale bar, 200 µm). (D) Alizarin Red S stain was extracted from the cells and quantified by measuring the absorbance at 570 nm. The effect of LS on the expression of transcription factors involved in osteoblast differentiation was also determined. (E) Protein expression of RUNX2 and BMP-2 were examined by western blot analysis. (F) The protein expression levels of each marker were normalized to actin. (G) mRNA levels of RUNX2, ALP (alpl), OPN (Spp1), OSN (Sparc), COL1 (Col1a1) and BSP (Ibsp) were analyzed using reverse transcription semi-quantitative PCR. (H) The mRNA expression levels of each factor was normalized to GAPDH. The results are presented as the means ± standard error of the mean (n=3). ##P<0.01 vs. growth cells; *P<0.05 and **P<0.01 vs. differentiated cells. LS, Leonurus sibiricus L.; RUNX2, runt-related transcription factor 2; BMP-2, bone morphogenetic protein 2; ALP, alkaline phosphatase; OPN, osteopontin; OSN, osteonectin; COL1, type I collagen; BSP, bone sialoprotein.