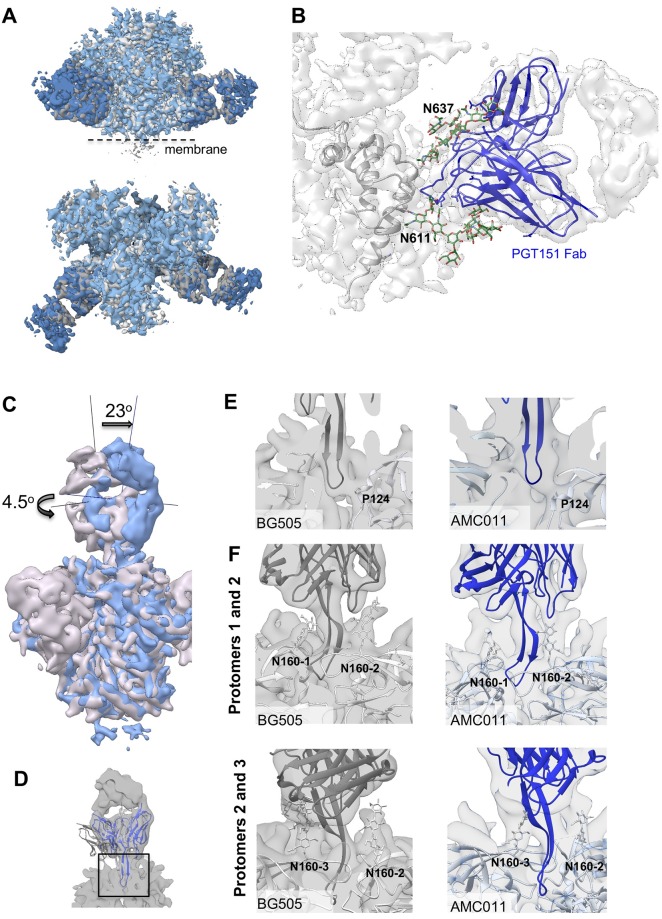
Fig 5. Binding of PGT145 Fab or PGT151 Fab to full-length AMC011 trimer.
(A) Superimposition of the cryo-EM map of the full-length AMC011 Env bound to PGT151 Fab (blue) and the JR-FL ΔCT trimer bound to PGT151 Fab low-pass filtered at 4.2 Å (gray, Lee et al., 2016). (B) Close-up of the PGT151 epitope. Coloring is as follows: glycans are depicted in green, PGT151 Fab in blue and the cryo-EM reconstruction density in white. (C) Superimposition of the cryo-EM map of and AMC011 full-length trimer bound to PGT145 and BG505 SOSIP.664 bound to PGT145 low-pass filtered to 5.7 Å. The vertical and horizontal axes were used to compare tilt and rotation angle between both PGT145 Fabs. (D) Close-up of the PGT145 epitope. The crystal structure of the PGT145 Fab (PDB: 3U1S) was docked into both cryo-EM maps for epitope comparison. The cryo-EM map of full-length AMC011 trimer bound to PGT145 is shown in white. (E) Cross sections of the PGT145 epitope (box in (D)) in BG505 SOSIP (gray) and AMC011 full-length (blue) trimers. Residue Pro124 of the trimer is shown in stick as a direct contact with the Fab. (F) Distribution of N160 glycans in the PT145 epitope of BG505 SOSIP and AMC011 full-length trimer. PGT145 Fab crystal structure (dark gray and dark blue for BG505 and AMC011, respectively) was docked into cryo-EM maps of BG505 SOSIP (EMD-8644) and AMC011 full-length trimers. The first sugars of the N160 glycan are indicated in sticks.