Fig. 5. Nrf2-dependent lung transcriptome changes by hyperoxia (O2).
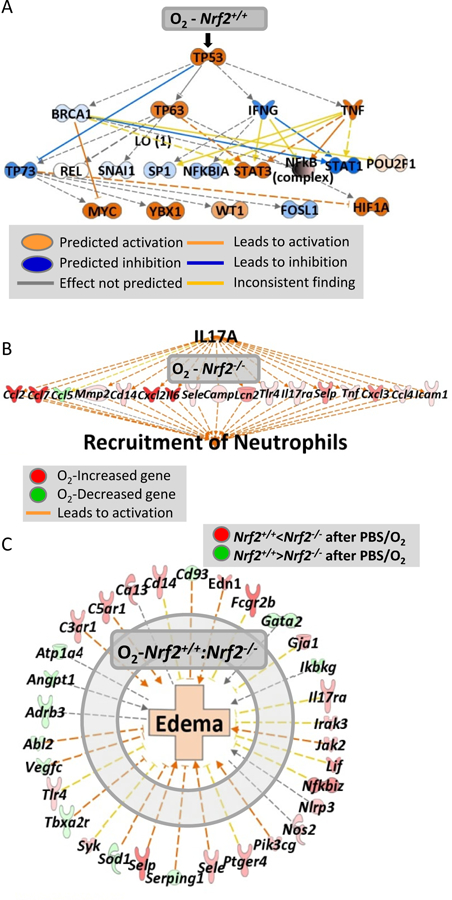
(A) Pathway analysis for hyperoxia-responsive genes in PBS-received Nrf2+/+ mice (n= 7162 genes, P < 0.01, Moderated t-test) demonstrated p53 as a key upstream regulator for the hyperoxia-altered lung genes, which may sequentially modulate other signal transducers. (B) In Nrf2−/− mice that received PBS, O2 altered genes (n = 4,799, P < 0.01) involved predominantly in IL-17A signaling pathway, which may lead to severe neutrophil infiltration. (C) Nrf2-dependently modulated genes during hyperoxia (n = 816, P < 0.01) such as Selp and Fcgr2b may contribute to the differential lung edema between Nrf2+/+ and Nrf2−/− mice given PBS.
