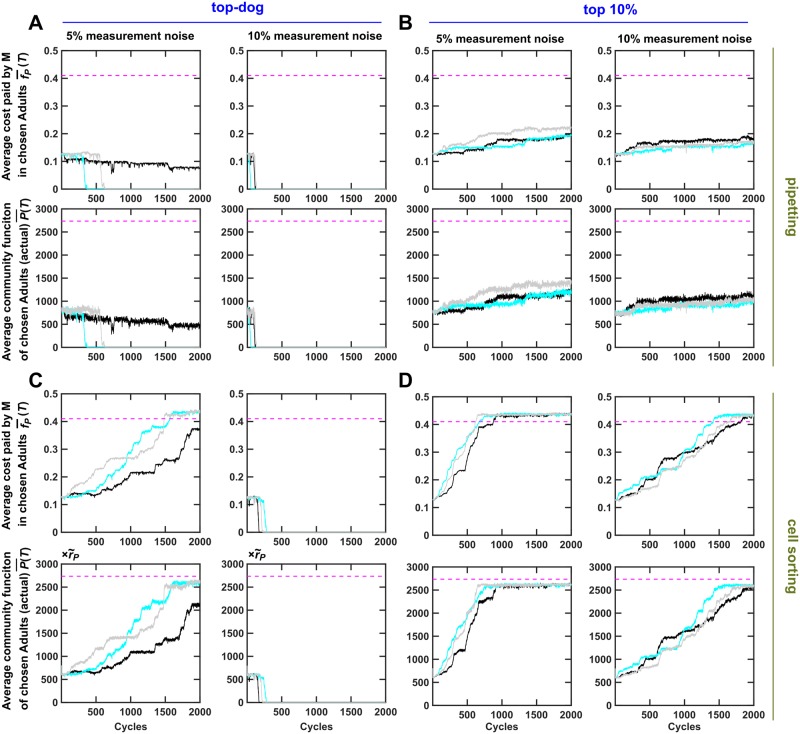
Fig 5. Ineffective selection due to community function measurement noise can be rescued by the top-tier strategy acting in synergy with cell sorting.
Adult communities were chosen to reproduce based on "measured community function P(T)"—the sum of actual P(T) and a "noise term" randomly drawn from a normal distribution with zero mean and standard deviations of 5% or 10% of the ancestral P(T). Dynamics of average fP and average community function of the chosen Adult communities ( and ) are plotted. When community function measurement noise is low (5%), cell sorting largely rescues ineffective community selection (A–D, left panels). When community function measurement noise is high (10%), both cell sorting and top-tier strategy are required (A–D, right panels). Black, cyan, and gray curves represent independent simulation trials. was averaged across the chosen Adults. was obtained by first averaging among M within each chosen Adult and then averaging across the chosen Adults. The simulation codes can be found in S3 Code, and the data can be found in S2 Data. Adult, Adult community; M, Manufacturer.