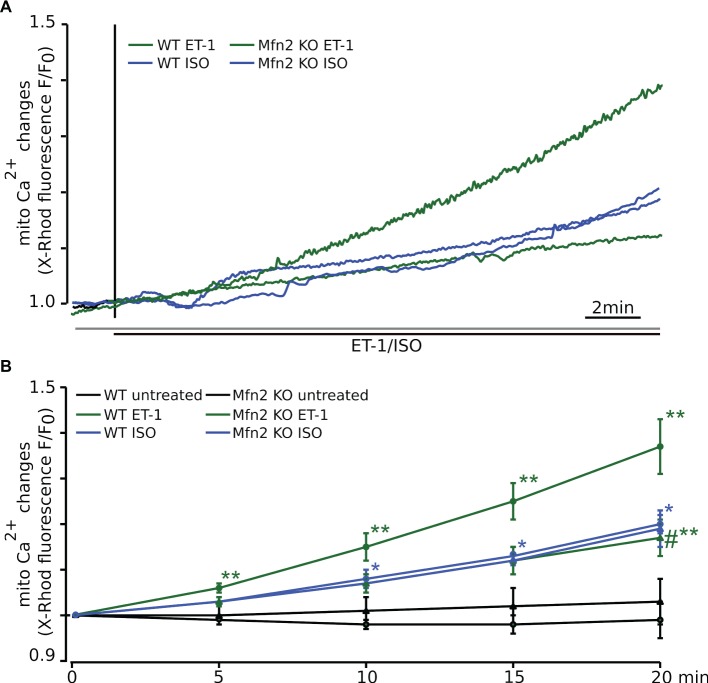
Figure 2.
In Mfn2 KO mice Ca2+ released via the IP3R cannot be taken up into mitochondria. (A) The representative confocal traces recorded from adult ventricular myocytes loaded with the Ca2+-sensitive fluorescent dye X-Rhod-1 upon electrical field stimulation (FS, 0.5 Hz) and subsequent exposure to 10 nM ET-1 (WT: solid green, Mfn2 KO: dashed green) or 500 nM ISO (WT: solid blue, Mfn2 KO: dashed blue), respectively. Changes in fluorescence reflect changes in mitochondrial Ca2+. (B) Mean values of the mitochondrial Ca2+ levels change during 20 min of observation. ET-1 increased mitochondrial Ca2+ concentration ([Ca2+]m) by +35 ± 6% (n = 7) in healthy WT myocytes, whereas ISO-induced elevation of [Ca2+]m was significantly smaller (+20 ± 2%, n = 7). In Mfn2 KO myocytes, the mitochondrial Ca2+ uptake induced by ET-1 was significantly smaller compared to WT myocytes (ET-1: +17 ± 4%, n = 9). However, the effect of ISO on mitochondrial Ca2+ uptake was not altered by Mfn2 KO (ISO: +19 ± 4%, n = 7). No significant changes in [Ca2+]m were observed in untreated WT (solid black) and Mfn2 KO (dashed black) myocytes during 20 min of observation. *p < 0.05 compared to untreated WT, **p ≤ 0.05 compared to untreated WT, #p ≤ 0.05 compared to WT treated with ET-1.