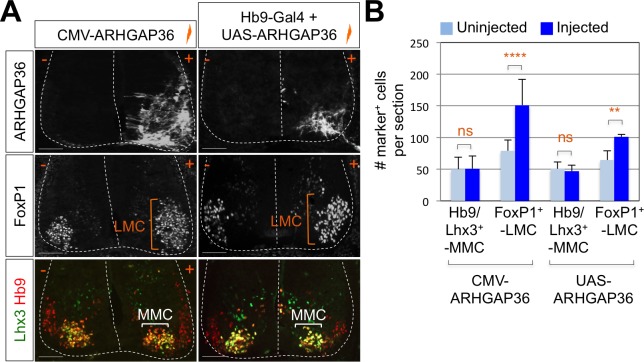
Figure 6. Expression of ARHGAP36 promotes LMC specification in developing chick spinal cord.
(A) ARHGAP36 constructs were injected and electroporated in chick neural tube and embryos (n = 8 ~ 15) were harvested 4 days post electroporation (four dpe). Ectopic expression of ARHGAP36 driven by CMV promoter in most injected cells induced robust expression of FoxP1+ LMC neurons (orange bracket) in ventral spinal cord but had no effect on MMC (Hb9+/Lhx3+) neurons (white bracket). Targeting the expression of ARHGAP36 specifically in motor neurons using Hb9-Gal4/UAS-ARHGAP36 system also lead to the robust induction of FoxP1+ LMC neurons (orange bracket) but had no effect on MMC (Hb9+/Lhx3+) neurons (white bracket). +, electroporated side; -, non-electroporated control side. Experiments were repeated independently at least three times. Scale bars: 100 μm. (B) Quantification of the number of FoxP1+ neurons and MMC (Hb9+/Lhx3+) neurons on the electroporated (+) and non-electroporated (-) sides of the spinal cord. Data are mean ± s.d. **p<0.001, ****p<0.00001; ns, non-significant (Student’s t-test). n = 6 ~ 20 independent images per each sample.