Figure 3: Key features of the drug-binding cavity in the hERG K+ channel pore.
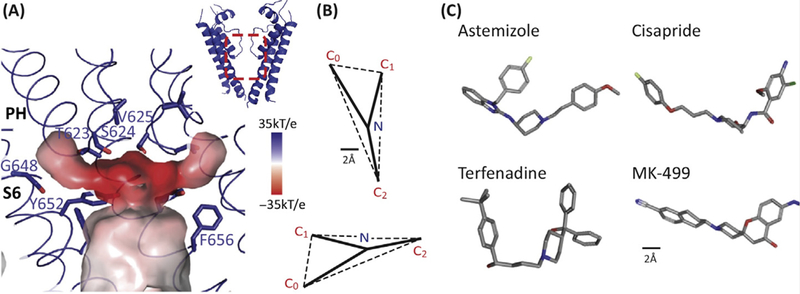
A. The central cavity of the pore domain was generated using Hollow (http://hollow.sourceforge.net). The colour scheme represents the electrostatic potential with the darker the red the more negative the electrostatic potential. There are four hydrophobic pouches (one per subunit) extending from the central cavity. Whilst the central cavity has a smaller diameter than that seen for the open conformation of other voltage-gated K+ channels, the hydrophobic pouches would create a much larger drug-binding cavity. Figure reproduced with permission from Figure 5 of [10].
B. Pharmacophore for hERG drug binding adapted with permission from [41]. The size bar is 2Å with the pharmacophore scaled to match the dimensions of the structure shown in panel A.
C. 3D conformers for 4 potent hERG K+ channel blockers taken from PubChem (https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/): Astemizole (CID: 2247), Cisapride (CID: 2769), Terfenadine (CID: 5405) and MK-499 (CID: 9934294).
