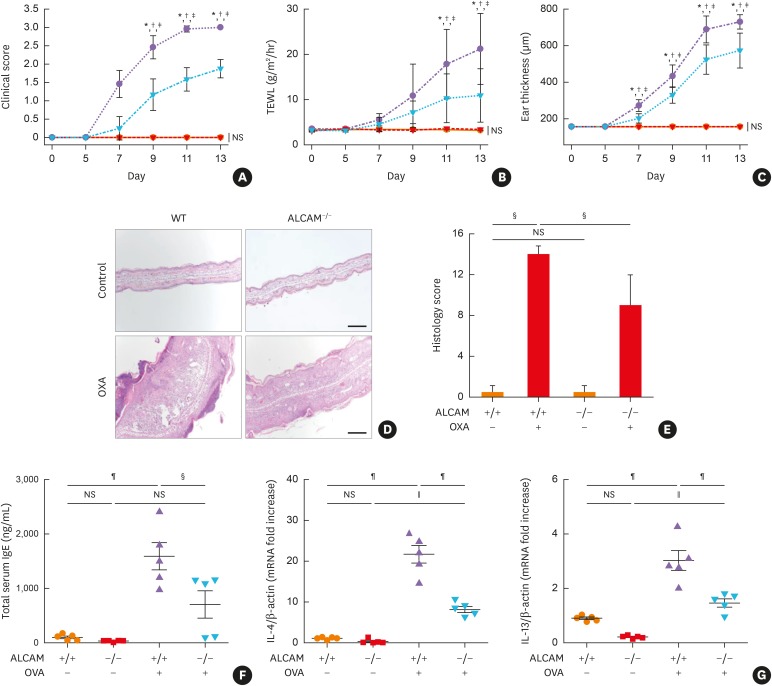
Fig. 5. ALCAM deficiency attenuates murine AD-like skin lesion induced by repeated OXA application. (A-C) AD severity was assessed by (A) clinical score, (B) TEWL and (C) ear thickness. (D) Mouse ear skin biopsy specimen stained with hematoxylin and eosin (×100, bar = 200 μm) and (E) scored according to histological features. (F) Total IgE level in serum, as determined by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. The mRNA expression of (G) IL-4 and IL-13 in skin lesions.
Data represent mean ± standard error of the mean.
ALCAM, activated leukocyte cell adhesion molecule; OXA, oxazolone; AD, atopic dermatitis; mRNA, messenger RNA; NS, not significant; WT, wild-type; TEWL, transepidermal water loss; IgE, immunoglobulin E; IL, interleukin, PBS, phosphate-buffered saline.
*P < 0.05 (WT/PBS vs. WT/OXA); †P < 0.05 (ALCAM−/−/PBS vs. ALCAM−/−/OXA); ‡P < 0.05 (WT/OXA vs. ALCAM−/−/OXA); §P < 0.05; ∥P < 0.01; ¶P < 0.001 (n = 4–6 mice/group).