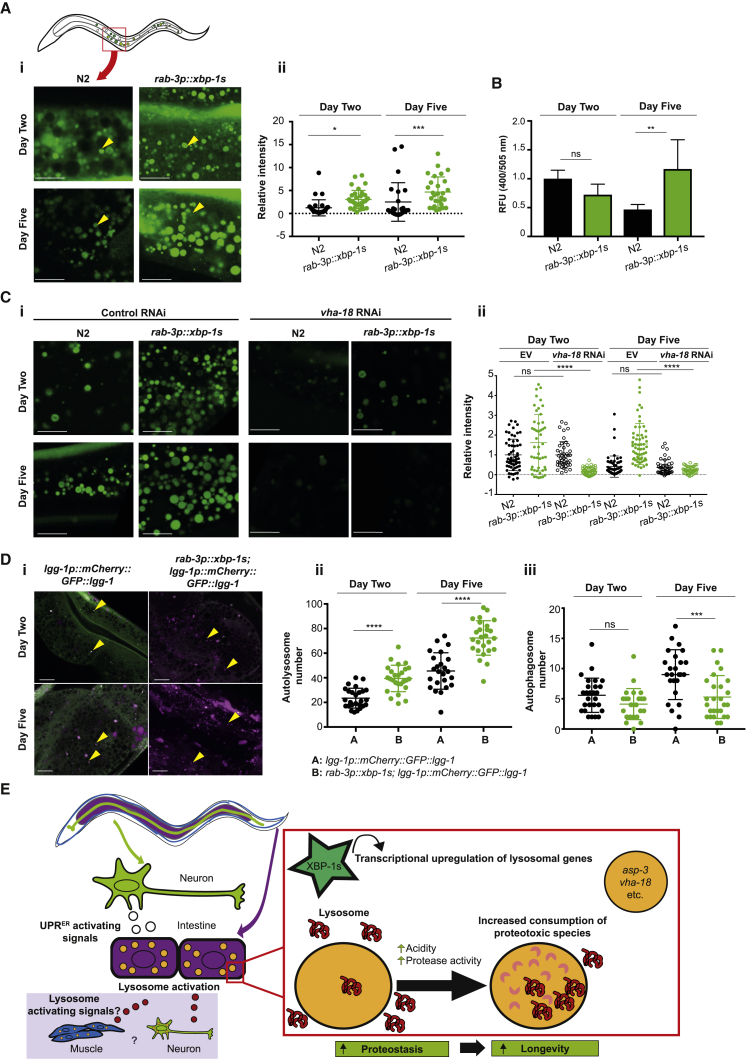
Figure 7.
Neuronal xbp-1s Increases Lysosomal Acidity
(A) (i) Confocal imaging of lysosomal acidity in N2 and rab-3p::xbp-1s intestines. Animals were grown on OP50 and transferred to plates containing cDCFDA 16 h prior to imaging. Imaging was conducted in the anterior intestine at 63× magnification in day 2 and day 5 adults. Yellow arrowheads indicate representative lysosomes. Scale bar, 10 μm.
(ii) Quantification of lysosomal acidity in wild-type and rab-3p::xbp-1s intestines. Animals were grown on OP50 and transferred to plates containing cDCFDA 16 h prior to imaging; imaging was conducted as described above, and fluorescence quantified from 3 experiments using ImageJ. Plots represent 5–10 animals per replicate. Significance was assessed between N2 and rab-3p::xbp-1s at each time point by one-way ANOVA with Tukey’s multiple comparisons, ∗p < 0.05, ∗∗∗p < 0.001.
(B) Protease activity in rab-3p::xbp-1s and N2 animals. Following incubation with a fluorescent substrate, relative fluorescence units (RFU) at 400/505 nm were measured. Bar graphs represent mean ± SD from 3 independent biological replicates. Significance was calculated using one-way ANOVA with Tukey’s multiple comparisons test; ns, not significant, ∗∗p < 0.01.
(C) (i) Confocal imaging of lysosomal acidity in N2 and rab-3p::xbp-1s animals grown on control (empty vector) or vha-18 RNAi and transferred to plates containing cDCFDA 16 h prior to imaging. Imaging was conducted as described above. Scale bar, 10 μm.
(ii) Quantification of lysosomal acidity in N2 and rab-3p::xbp-1s animals grown on control (empty vector) or vha-18 RNAi. Animals were imaged as above, and quantification of fluorescence from 3 experiments were carried out using ImageJ. Plots represent 8–10 animals per replicate. Significance was assessed between N2 and rab-3p::xbp-1s at each time point by one-way ANOVA with Tukey’s multiple comparisons, ∗∗∗∗p < 0.0001.
(D) (i) lgg-1p::mCherry::GFP::lgg-1 and rab-3p::xbp-1s; lgg-1p::mCherry::GFP::lgg-1 animals were grown on OP50 and imaged at days 2 and 5 of adulthood at X63 magnification. Arrowheads in lgg-1p::mCherry::GFP::lgg-1 indicate representative autophagosomes; arrowheads in rab-3p::xbp-1s; lgg-1p::mCherry::GFP::lgg-1 indicate representative autolysosomes. Scale bar, 10 μm.
(ii) Quantification of autolysosomes. mCherry::LGG-1-positive (magenta) punctae were counted in 10–15 worms per genotype at day 2 and day 5 of adulthood using ImageJ. Data are derived from 3 independent biological replicates. Statistical analysis was carried out using one-way ANOVA with Tukey’s multiple comparisons test, ∗∗∗∗p < 0.0001.
(iii) Quantification of autophagosomes. mCherry::LGG-1::GFP-positive (white) punctae were counted in 10–15 worms per genotype at day 2 and day 5 of adulthood using ImageJ. Data are derived from 3 independent biological replicates. Statistical analysis was carried out using one-way ANOVA with Tukey’s multiple comparisons test, ∗∗∗p < 0.001.
(E) Schematic of the regulation of lifespan and proteostasis by neuronal and intestinal xbp-1s through increased lysosome activity. See also Figure S7.