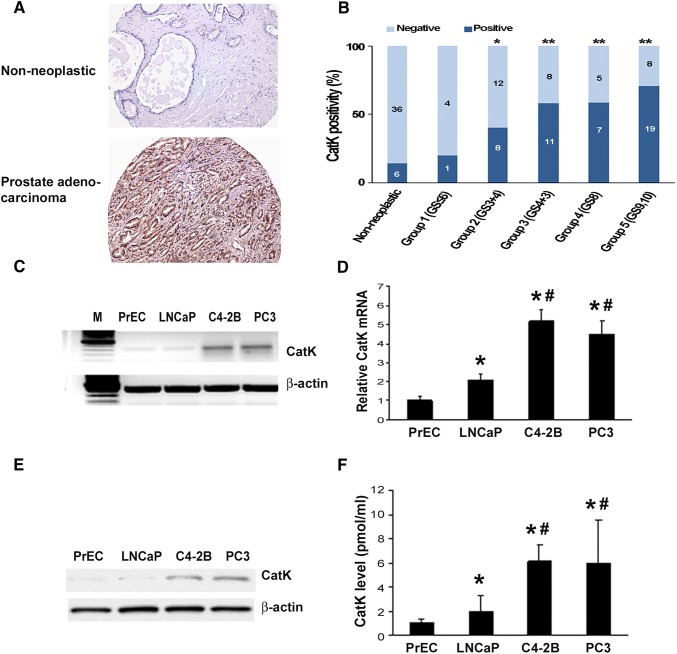
Fig. 1.
CatK mRNA and protein expression in PCa tissues and cell lines. a CatK expression in human PCa tissues. Immunohistochemical staining was performed for detection of CatK in human PCa and corresponding non-neoplastic tissues. b Quantitative evaluation of CatK expression in PCa. Dark blue bars represent case number of CatK-positive staining, and light blue bars show case number of CatK-negative staining. Statistically significant differences were noted between PCa and corresponding non-neoplastic tissues. **P < 0.001 compared to non-neoplastic tissues. c Total RNA was extracted from prostate epithelial cells (PrEC), LNCaP, C4-2B, and PC3 cells, then subjected to RT-PCR for the detection of CatK mRNA. PCR product of 399 bp is detected. d Quantification of CatK mRNA determined by real-time PCR. Internal control is β-actin. *P < 0.05 compared to PrEC; #P < 0.01 compared to LNCaP cells. e To evaluate for CatK expression in the prostate cancer cells, confluent PrEC, LNCaP, C4-2B, and PC3 cells were washed with PBS and then lysed in RIPA buffer. Proteins were applied to SDS-PAGE followed by Western blot system with rabbit anti-human CatK polyclonal Ab, or mouse anti-human β-actin monoclonal Ab. The Ab binding was revealed using an HRP-conjugated anti-rabbit IgG, or HRP-conjugated anti-mouse IgG1 and enhanced chemiluminescence blot detection system. f To test CatK production in the PCa cell supernatants, CM collected from PrEC, LNCaP, C4-2B, and PC3 cell cultures were measured by an ELISA kit. *P < 0.01 compared to PrEC; #P < 0.01 compared to LNCaP cells