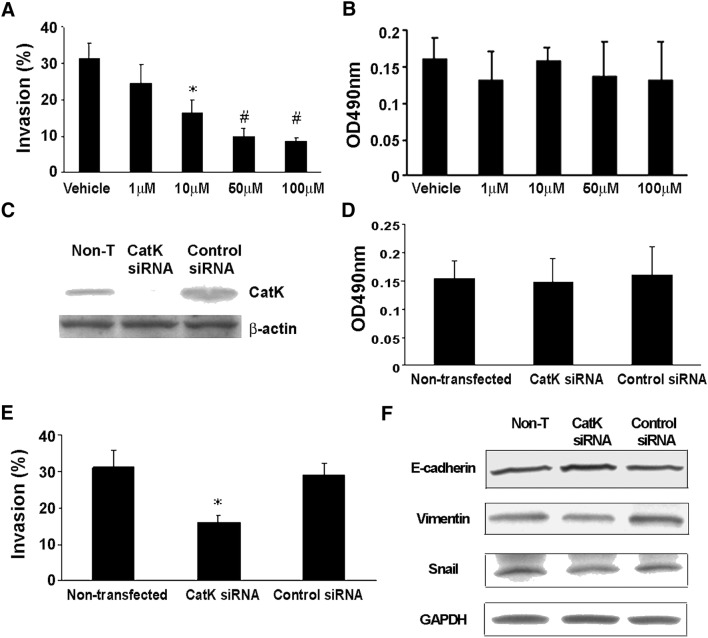
Fig. 2.
CatK inhibitor diminishes the invasiveness of C4-2B cells. a The in vitro invasion assay was performed using C4-2B cells cultured in 24-well transwell chambers (BD BioCoat Matrigel Invasion Chamber, BD Biosciences, MA), as directed by the manufacturer. Invasive ability was defined as the proportion of cells that penetrated the matrix-coated membrane divided by the number of cells that migrated through the uncoated membrane (baseline migration). The results are reported as the mean of triplicate assays. *P < 0.05 compared to the vehicle; #P < 0.001 compared to the vehicle. b The C4-2B cells viability were examined by MTS assay. C4-2B cells were treated with various doses of CatK inhibitor (the doses that were used in the tumor invasion assay). We did not observe any significant differences among these cells in terms of cell viability. c The designed CatK siRNA or scrambled control siRNA were transfected into C4-2B cells using the transfection reagents. Cell lysates were collected for Western blot to confirm CatK expression was knocked down. d CatK expression knockdown cell viability was measured. There was no significant change among the parental cells and cells that transfected with CatK siRNA or control siRNA. e The ability of CatK expression knockdown cell invasion was examined. Knockdown CatK expression decreased C4-2B cell invasion. The results are reported as the mean of triplicate assays. *p < 0.01 compared to the control siRNA-transfected cells. f E-cadherin, Vimentin and Snail expression levels were detected by Western blot in CatK knockdown cells and the controls