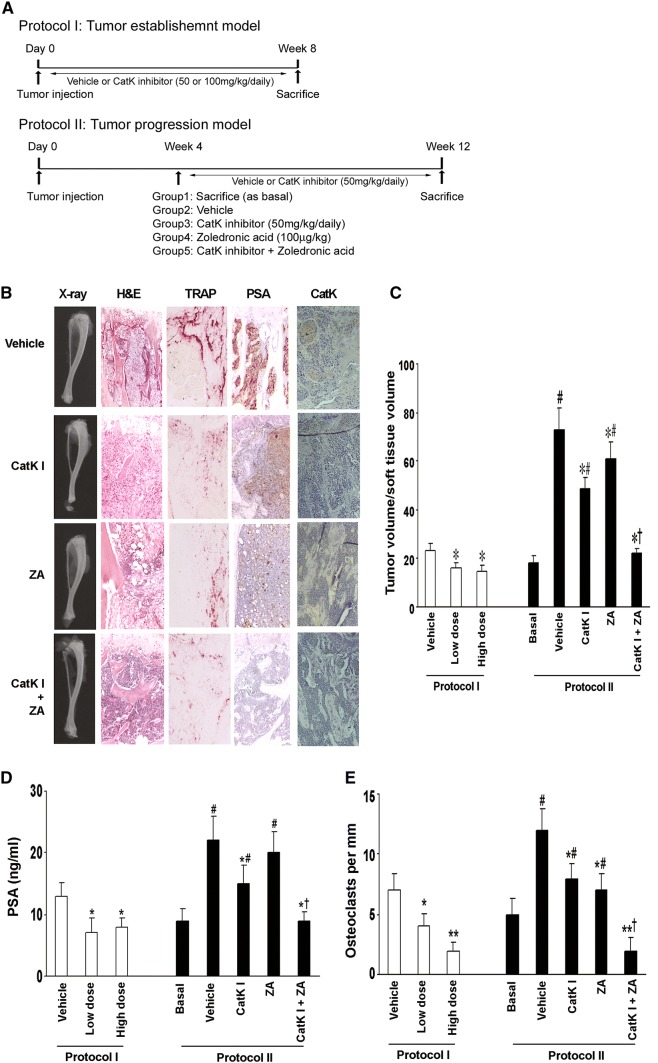
Fig. 4.
CatK inhibitor prevents the establishment and retards the progression of PCa tumor in mouse bone. a Schematic of experimental procedures to determine the effects of CatK inhibitor on the establishment and progression of prostate cancer. Mice were killed at the end of experiments. X-ray, H&E, and PSA were determined. b In this representative figure, note the area of osteolysis and osteosclerosis of the vehicle-treated mouse compared to the radiograph of the CatK inhibitor-treated mouse. PSA is strongly positive in all vehicle-treated mice compared to CatK inhibitor-treated mice. After CatK inhibitor treatment, TRAP-positive cells were apparently reduced in the tibiae compared to the vehicle group (for the tumor progression model, we observed the similar results). c Tumor volume versus non-bone soft tissue volume was measured by bone histomorphometry. d Serum PSA levels in the mice model were measured by ELISA and found CatK inhibitor decreased serum levels. e Osteoclast numbers per millimeter bone surface were quantified by bone histomorphometry. Results are reported as mean ± SD. *P < 0.01 compared to vehicle group; #P < 0.01 compared to the basal group