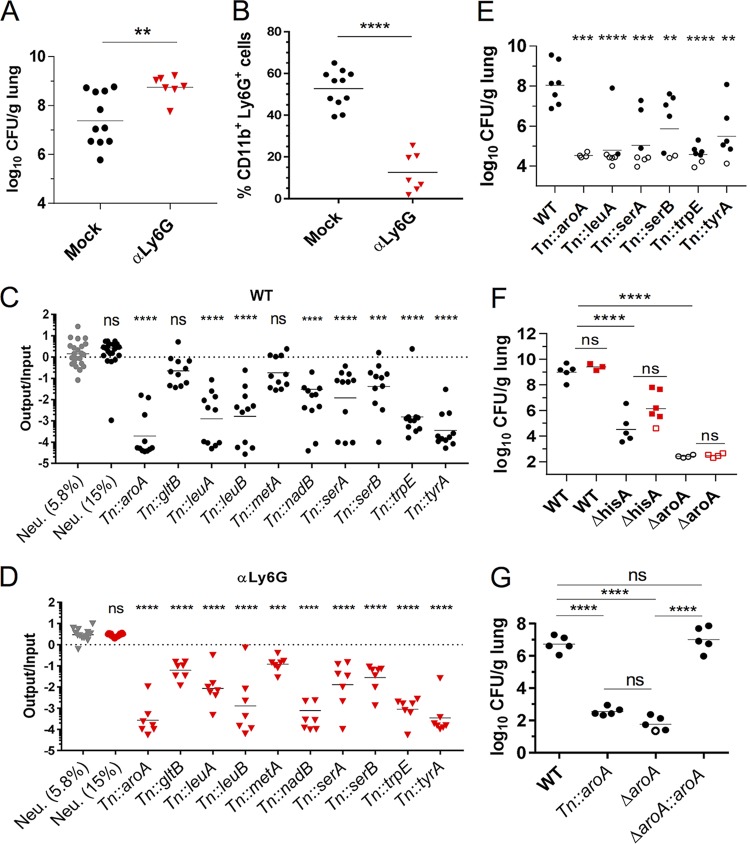
FIG 2.
K. pneumoniae genes encoding enzymes required for amino acid biosynthesis are attenuated in the lungs of WT and neutropenic mice. (A to D) Mock-depleted and αLy6G mice were infected with 2 × 104 CFU of a minilibrary of K. pneumoniae Tn mutants and sacrificed at 33 hpi. (A) CFU/g lung for each mouse. (B) Percent PMN population (Ly6G+ CD11b+) per live cells. (C and D) Abundance of each Tn strain in the output versus the input pool in mock-depleted (C) and αLy6G (D) mice. (E) CFU in lungs of mice infected with 1 × 103 CFU of the indicated strains and sacrificed at 45 hpi. (F) CFU in lungs of Mock-depleted (circles) and αGr1 (squares) mice infected with 2 × 103 CFU of the indicated strains and sacrificed at 40 hpi. (G) CFU of mice infected with 2 × 104 CFU of the indicated strains and sacrificed at 33 hpi. Each symbol represents a mouse; open symbols indicate no CFU were recovered and limit of detection, and dashes represent geometric mean (A, C to G) or mean (B). Each strain was tested in two to four mice per cohort in at least two independent experiments. The data are combined from all experiments. Statistical significance was determined by Student t test (A and B) on log transformed (A) and nontransformed (B) values or by one-way ANOVA with Dunnett’s posttest (C and D) on log-transformed values by comparing each mutant against the neutral mutants present at 5.8% in the input pool. To assess whether Tn mutants had statistically significant fitness differences in αLy6G mice compared to WT, the fitness of each mutant in WT mice was compared to the fitness of the same mutant in αLy6G mice using one-way ANOVA with Dunnett’s posttest. No mutants had a significantly higher value in αLy6G mice than WT. (E to G) One-way ANOVA on log-transformed values using Dunnett’s (E) or Tukey’s (F and G) posttests. **, P < 0.01; ***, P < 0.001; ****, P < 0.0001.