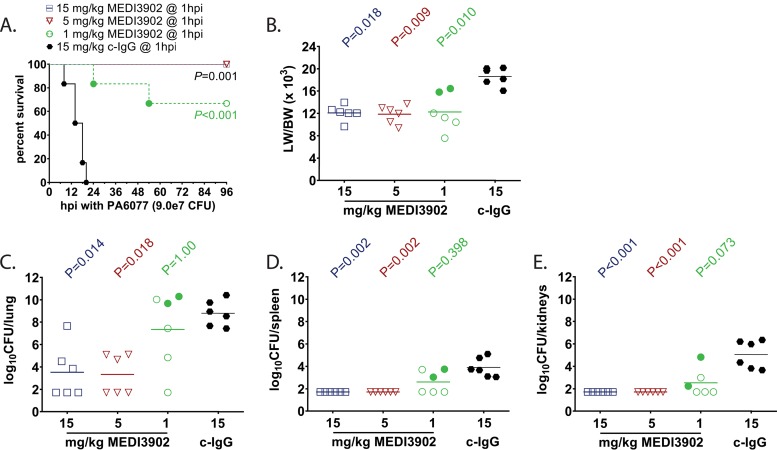
FIG 2.
Treatment with MEDI3902 improves survival outcomes in a dose-dependent manner in a rabbit acute pneumonia model. (A to E) Comparisons of Kaplan-Meier survival curves (A), lung weight-to-body weight (LW/BW ×103) ratio (B), log10 CFU/lung (C), log10 CFU/spleen (D), and log10 CFU/kidneys (E) for rabbits intravenously administered 15 mg/kg MEDI3902 (n = 6), 5 mg/kg MEDI3902 (n = 6), 1 mg/kg MEDI3902 (n = 6), or 15 mg/kg control IgG (n = 6) at 1 h postinfection (hpi). A one-sided log rank (Mantel-Cox) test was used to evaluate survival. LW/BW and bacterial densities for animals treated at 1 h postinfection with control IgG were compared to those treated with different concentrations of MEDI3902 by nonparametric one-way ANOVA with Kruskal-Wallis test, followed by Dunn’s multiple-comparison test. Filled symbols represent data from dead animals, and open symbols represent data from surviving animals that were euthanized at 96 h postinfection.