Fig. 3.
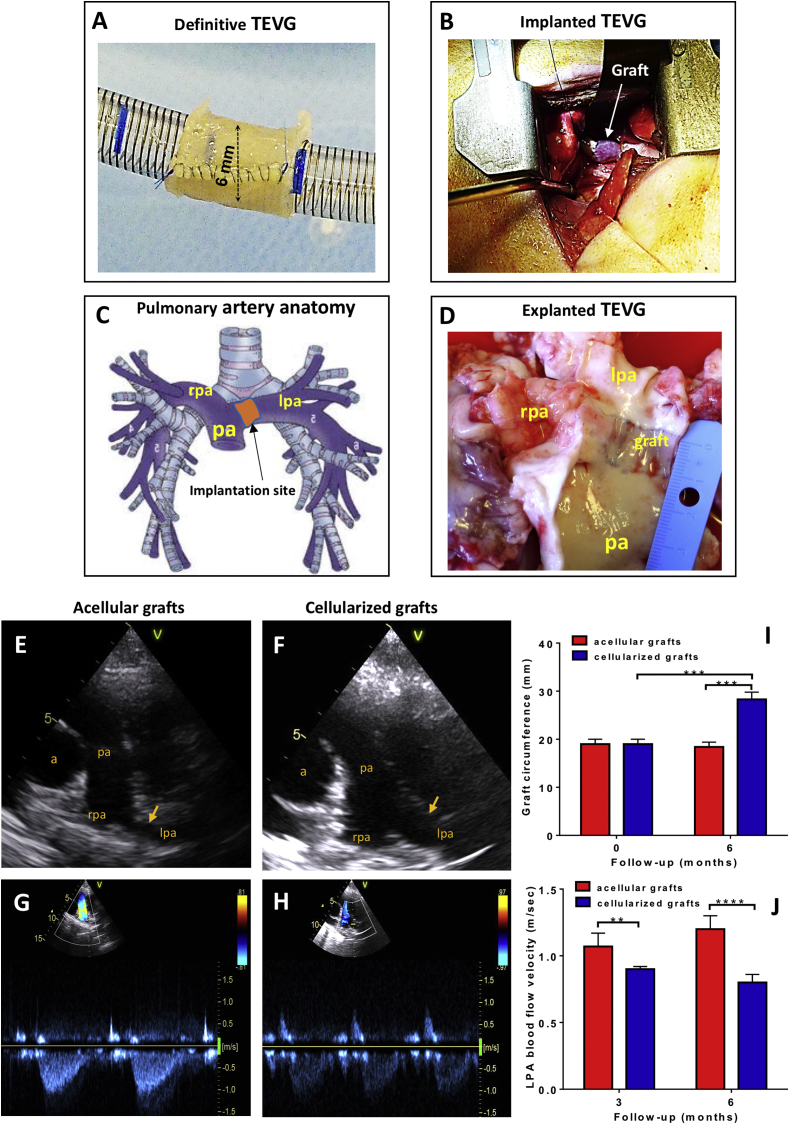
Outcome of the preclinical trial. (A&B) The cell engineered graft was shaped into a 6 mm diameter conduit with 10 mm length (A) and implanted into swine left pulmonary artery (B). (C) Anatomy of the main pulmonary artery and its major branches. Arrow indicates the position of TEVG implantation. (D) Representative image of the explanted TEVG with main pulmonary artery (pa) and left pulmonary artery (lpa) cut-open to show the luminal side. The graft is marked by the blue anastomosis sutures (rpa, right pulmonary artery). Representative ultrasound images of the pulmonary arteries of acellular and cellularized grafts. Arrows indicate level of graft insertion (a, aorta; pa, pulmonary artery; rpa, right pulmonary artery; lpa, left pulmonary aretry). (G&H) Representative images of Colour Doppler blood velocities in acellular and cellularized groups. (I) Circumference of the cellularised and acellular grafts at implantation and six months post-surgery. ANOVA with post-hoc testing were used. ***p < 0.001. (J) Blood flow velocities through the acellular and cellularized LPA at 3 and 6 months of follow-up. ANOVA with post-hoc testing were used. **p < 0.01. ***p < 0.001.