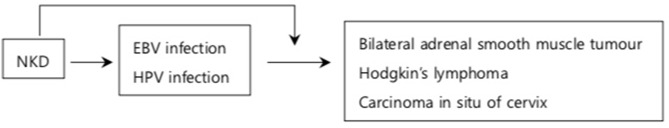
Figure 1.
NKD and viral induced cancer. NKD results in reduced number of NK cells (11) and downregulation of activating receptors against oncogenic viruses (24). This increases the susceptibility to EBV and HPV infections which subsequently progress into cancer (27–31). In addition, NKD compromises cytotoxicity against viruses during the infection allowing viral genes to be transfected into infected cells which transform into cancerous cells (23, 25). The arrows indicate the increased risk of developing conditions on the box that it is pointing to.