Figure 10.
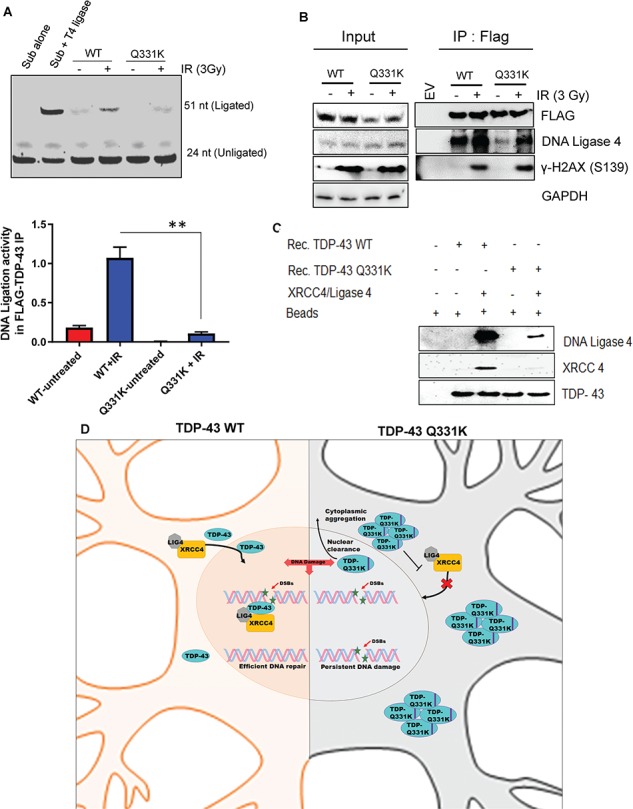
The Q331K mutation affects DNA-ligation activity. (A) In vitro DNA-ligation assay using extracts of neurons expressing WT or mutant TDP-43 before and after DNA damage induction by IR (3 Gy). Quantitation of DNA-ligation activity from three independent experiments expressed as fold change in the histogram. (B) IP of WT- and Q331K-expressing cells with anti-FLAG antibody or IgG (mouse) before and after DNA-damage induction by IR (3 Gy) shows reduce DNA ligase 4 interaction in Q331K mutant cells. (C) His-affinity pulldown assay using recombinant TDP-43-WT and TDP-43-Q331K shows reduced association of the Q331K protein with XRCC4-DNA ligase 4 complex in vitro. (D) A model showing TDP-43 WT facilitates XRCC4-Ligase4 complex nuclear translocation in healthy neuronal cells leading to efficient DNA repair. ALS-linked Q331K mutation nuclear clearance and cytoplasmic aggregation impairs XRCC4-Ligase4 complex nuclear translocation leading to persistent DNA damage accumulation. **P<0.05.
