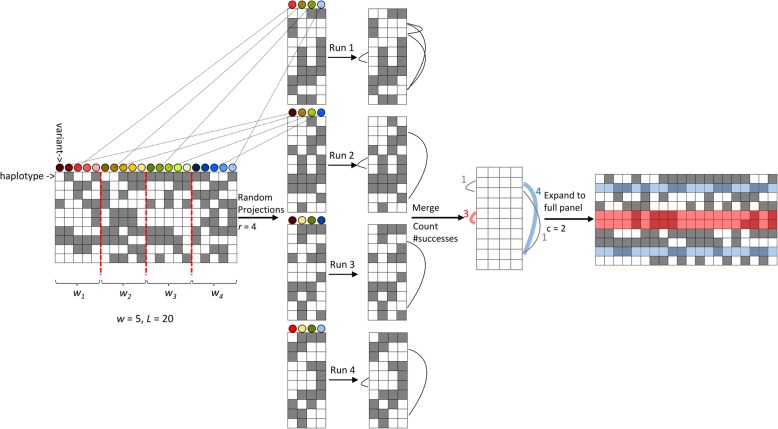
Fig. 1.
Schematic of the RaPID algorithm. The first step of RaPID is multiple random projections of the input phased genotype panel by selecting a random variant site per window (wi). The second step is running PBWT for each of the projected panels to identify exact matches of subsequences with a length above a certain cutoff. In the third step, exact matches are collected and only those regions reporting more than a certain number are selected to be a candidate IBD segment. The length cutoff (L) was set to 10, the window size (w) was set to 5, the number of runs (r) was set to 4, and the number of successes (c) was set to 2. Four different matches were detected, two of them only in one run and two in more than two runs (depicted in blue and red). Two matches with only one success are discarded