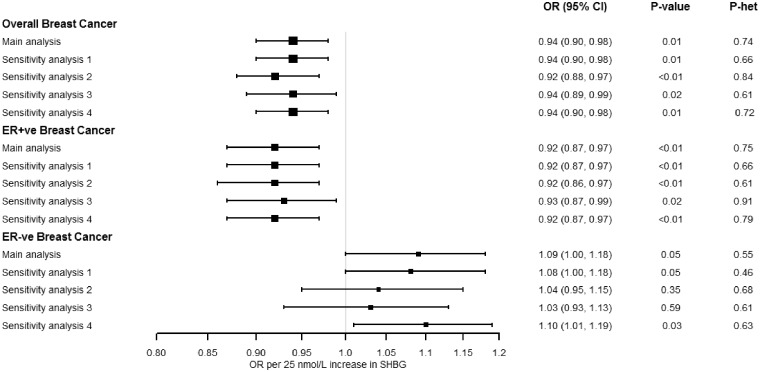
Figure 2.
Multivariable inverse-variance weighted Mendelian randomization estimates between sex hormone binding globulin (SHBG) concentrations and risk of breast cancer, adjusting for the genetic effects of body mass index (BMI). Main analysis: the odds ratios represent increase/decrease of risk per 25nmol/L increase in SHBG levels (N = 12 SNPs). Sensitivity analysis 1: we used 11 SNPs after excluding rs780093 due to potential pleiotropy with several other traits.41–44 Sensitivity analysis 2: we used nine SNPs after excluding rs1641537, rs1625895 and rs3779195 derived from conditional analyses in the GWAS of SHBG.20 Sensitivity analysis 3: we used as instruments only the three SNPs (i.e. rs12150660, rs7910927, rs780093), which were significant in the GWAS analysis for SHBG only in women.20 Sensitivity analysis 4: we used female-specific estimates for the SNP-SHBG associations (for three SNPs i.e. rs1641537, rs1625895 and rs3779195, estimates were only reported in males and females together).20.