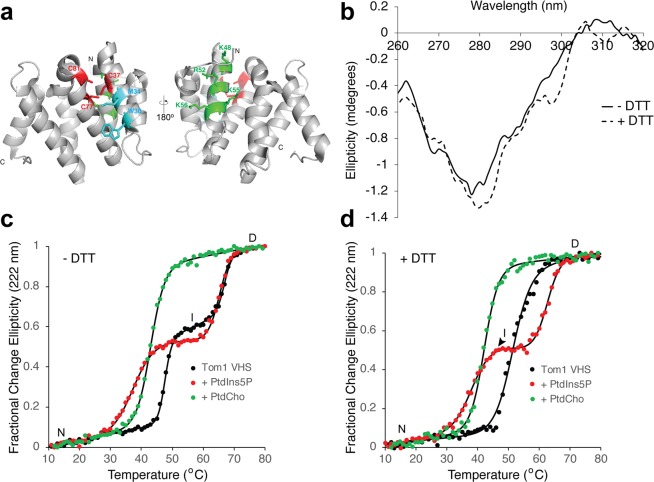
Figure 2.
Effect of phospholipids on the thermal stability of the Tom1 VHS domain. (a) Two views of the cartoon representation of the Tom1 VHS domain indicating the location of the three conserved cysteine residues (red) and the putative PtdIns5P (green) and ubiquitin (cyan) binding sites. (b) Near-UV CD spectra of Tom1 VHS in nonreducing and reducing conditions. (c) Thermal denaturation of the Tom1 VHS domain under nonreducing conditions in the absence (black circles) and presence of a molar excess of PtdIns5P (red circles) or PtdCho (green circles). Results from one representative CD measurement of the protein are shown in the figure. Data were fitted to the merged points using a two-state denaturation model for PtdCho-bound Tom1 VHS or the three-state denaturation model for free or PtdIns5P-bound Tom1 VHS. (d) Thermal denaturation of the Tom1 VHS domain under reducing conditions in the absence (black circles) and presence of a molar excess of PtdIns5P (red circles) or PtdCho (green circles). Results from one representative CD measurement of the protein are shown in the figure. Data were fitted to the merged points using a two-state denaturation (free or PtdCho-bound Tom1 VHS) or three-state denaturation (PtdIns5P-bound Tom1 VHS) state models.