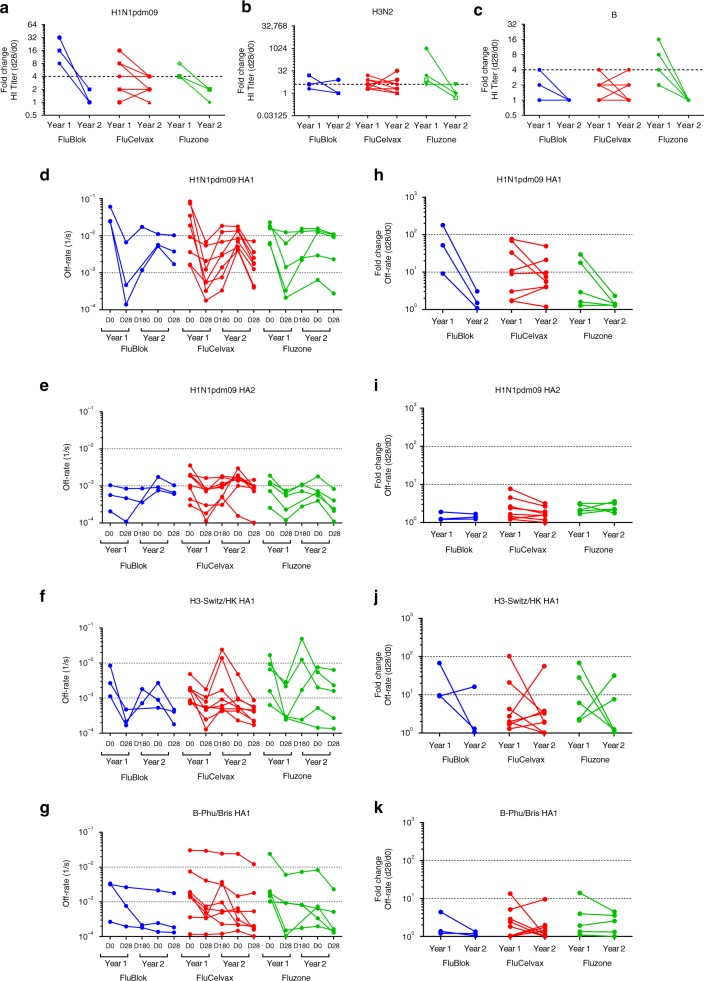
Fig. 4.
Impact of repeat vaccination on HI titers and antibody affinity maturation. a–c Fold change in end-point titers are calculated by dividing post-vaccination (D28) titers by pre-vaccination (D0) titers of respective years for HI against H1N1pdm09 (a), H3N2 (b), and influenza B (c) virus strains as shown for FluBlok (in blue), FluCelvax (in red), and Fluzone (in green) for each of the 16 repeatedly vaccinated individuals. d–k Sequential SPR analysis of human vaccine sera (pre- and post- vaccination) was performed against properly folded H1N1pdm09 HA1 (d) and HA2 (e) domains, and H3 HA1 (f) and B-HA1 (g). Ten-fold, 50- and/or 250-fold diluted individual serum from 16 repeatedly vaccinated participants at pre-vaccination (D0) and post-vaccination (D28; D180 for year 1 only) are evaluated as shown for FluBlok (in blue), FluCelvax (in red), and Fluzone (in green) for each subject in the first year (2015–2016; S1) and second year (2016–2017; S2). Serum antibody off-rate constants are determined as described in Methods. h–k Fold increase in antibody affinity was calculated [1/(off-rate on Day 28/off-rate on Day 0)] for respective years against H1N1pdm09 HA1 (h) and HA2 (i) domains, H3N2 HA1 (j) and B-HA1 (k). Source data are provided as a Source Data file