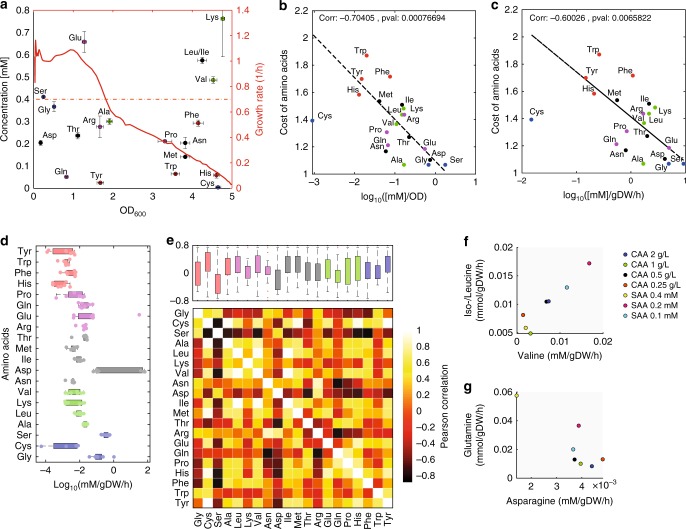
Fig. 4.
Consumption vs. cost of amino acids. a Each dot represents one amino acid, while the red line is the instantaneous cellular growth rate. For each amino acid, the initial concentration is related to the OD600 at which the amino acid has been depleted from the medium. b For each amino acid, its metabolic cost, i.e., the number of high-energy phosphate bonds required for biosynthesis41, is compared to the ratio between initial amino acid concentration and culture OD600 at time of depletion shown in a. c For each amino acid, its metabolic cost41 is compared to an average estimate of its uptake rate, calculated as the initial amino acid concentration divided by the hours and culture gram of dry biomass (gDW) at time of amino acid depletion. d Distribution of amino acid average uptake rates across seven media containing different initial quantities of amino acids (see also Supplementary Fig. 12). e Heatmap of pairwise correlation between average uptake rates of amino acids across seven tested conditions. Boxplot of pairwise correlation for each amino acid. Box edges correspond to 25th and 75th percentiles, whiskers include extreme data points, and outliers are shown as red plus signs. f Average uptake rates of valine against iso-/leucine. g Average uptake rates of asparagine against glutamine