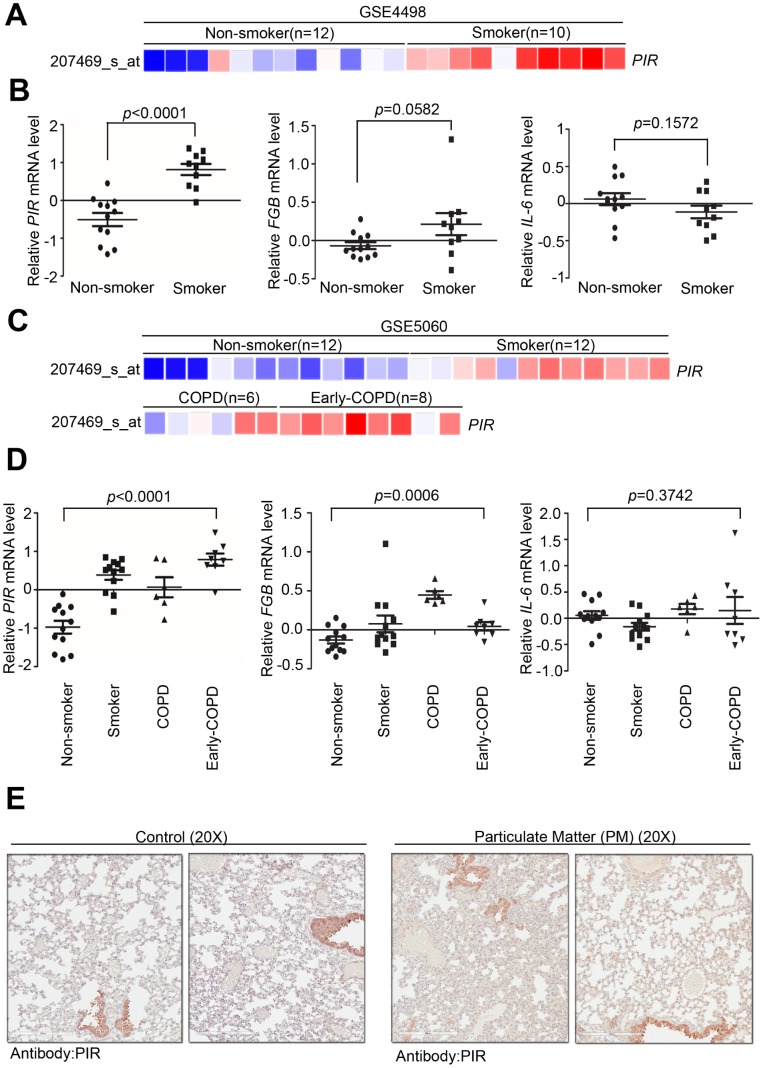
Figure 5.
Overexpression of PIR correlates with smoke and early COPD. (A) Detailed heatmap highlights the correlation between the mRNA expression level of PIR and smoke in the GSE4498 cohort (n = 22) using Oncomine online analysis tool. (B) Differential mRNA levels of PIR, FBG, and IL-6 between non-smoker and smoker in the GSE4498 cohort. (C) Detailed heatmaps highlight the correlation between the mRNA expression levels of PIR and non-smoker, smoker, COPD, and early COPD in the GSE5060 cohort (n = 38) using Oncomine online analysis tool. (D) Differential mRNA levels of PIR, FBG, and IL-6 in non-smoker, smoker, COPD, and early COPD in the GSE5060 cohort (n = 38) in the analysis by the Oncomine online analysis tool. (E) The immunohistochemical staining results showed PM-fed mice group had higher concentration of the PIR protein in the lung tissue.