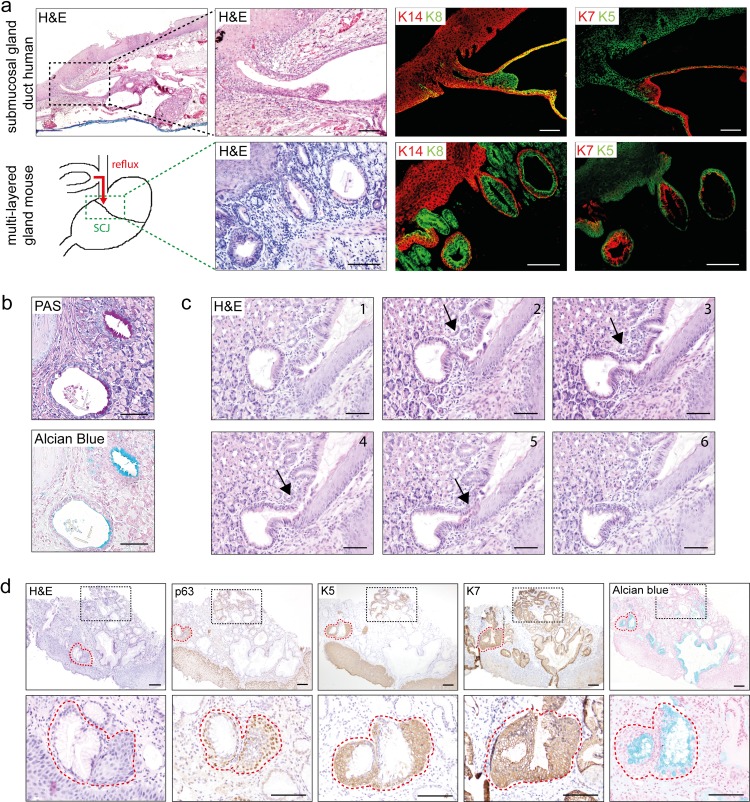
Fig 1. Mouse multi-layered glandular structures (MLGS) show homology to human esophageal submucosal glands ducts (SMGD) and human multi layered epithelium (MLE).
[a] Human esophageal submucosal gland (SMG) duct (black dotted box) and mouse MLGS at the SCJ (green dotted box) upon bile stimulation. IF staining for squamous markers K14 (red) and K5 (green) and columnar markers K8 (green) and K7 (red). [b] PAS and Alcian blue staining of multi-layered glandular structures (MLGS) at the SCJ. [c] Serial sections of a MLGS at the SCJ in mice with bile reflux, which extends towards the surface (arrow). [d] IHC for p63, K5, K7 and Alcian blue staining of human early non-goblet cell columnar metaplasia (red dotted line) arising from submucosal multi-layered glandular structures (black dotted box), human esophageal SMGD and murine MLGS. (Scale bars 100μm).