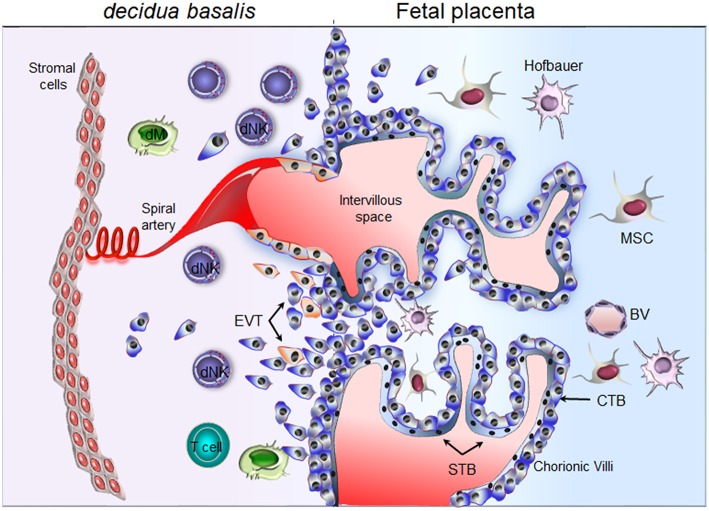
Figure 1.
Schematic representation of the maternal-fetal interface. Floating chorionic villi are bathed in maternal blood within the intervillous space. A multinucleated syncytiotrophoblast (STB) outer cell layer covering the chorionic villi. STB layer serves for transport of nutrient and barrier function. A layer of cytotrophoblast cells (CTBs), underlines the STB. CTBs differentiate into extravillous trophoblast (EVTs) and invade the maternal decidua. Through the release of soluble factors (cytokines, chemokines, and proangiogenic factors), maternal decidual NK (dNK) cells participate actively in the attraction of invasive EVTs and remodeling of the spiral arteries. Invasive EVTs are also in contact with decidual macrophages (dM) and T cells. Fetal blood vessel (BV), mesenchymal stem cells (MSC), Hofbauer cells (fetal macrophage).