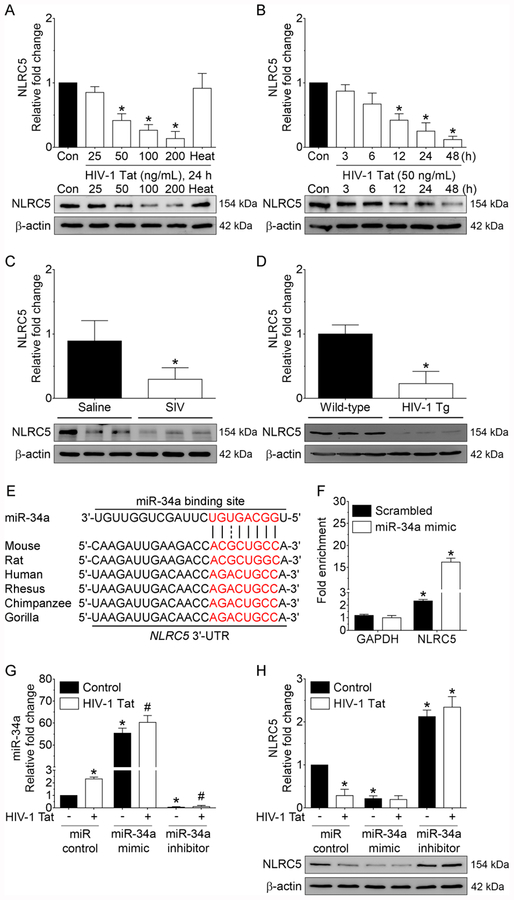
FIGURE 2.
Downregulation of NLRC5 both in vitro and in vivo. Representative western blotting analysis showing the dose-dependent (A) and time-dependent (B) downregulation of NLRC5 expression in HIV-1 Tat exposed mouse primary microglial cells. Data are mean±SEM from six independent experiments. Nonparametric Kruskal–Wallis one-way ANOVA followed by Dunn’s post hoc test was used to determine the statistical significance of multiple groups. *p < 0.05 versus control. Con, Control. (C) Representative western blotting analysis showing decreased expression of the NLRC5 protein in the medial prefrontal cortices of SIV-infected rhesus macaques compared with the saline group. Data are mean ± SEM. An unpaired Student’s t test was used to determine the statistical significance. *p < 0.05 versus saline. (D) Representative western blotting analysis showing decreased expression of the NLRC5 protein in the medial prefrontal cortices of HIV-1 transgenic rats compared with the wild-type rats. Data are mean ± SEM. An unpaired Student’s t test was used to determine the statistical significance. *p < 0.05 versus wild-type. (E) Putative miRNA-34a binding sites in the 3′-UTR of NLRC5 gene. (F) miRNA target validation assay confirmed enrichment of the miRNA-34a target mRNA, NLRC5 in Ago IP compared with total RNA isolated from mouse primary microglial cells transfected with miRNA-34a mimic or miRNA control. GAPDH was used as a housekeeping control. (G) qPCR analysis showing expression levels of miRNA-34a in mouse primary microglial cells transfected with miRNA control, miRNA-34a mimic or miRNA-34a inhibitor following exposure to HIV-1 Tat (50 ng/ml) for 24 h. (H) Representative western blotting analysis showing expression of the NLRC5 protein in mouse primary microglial cells transfected with control, miRNA-34a mimic or miRNA-34a inhibitor following exposure to HIV-1 Tat (50 ng/ml) for 24 h. β-Actin was probed as an internal control for all the experiments. Nonparametric Kruskal–Wallis one-way ANOVA followed by Dunn’s post hoc test was used to determine the statistical significance of multiple groups. *p < 0.05 versus control; #p < 0.05 versus HIV-1 Tat.