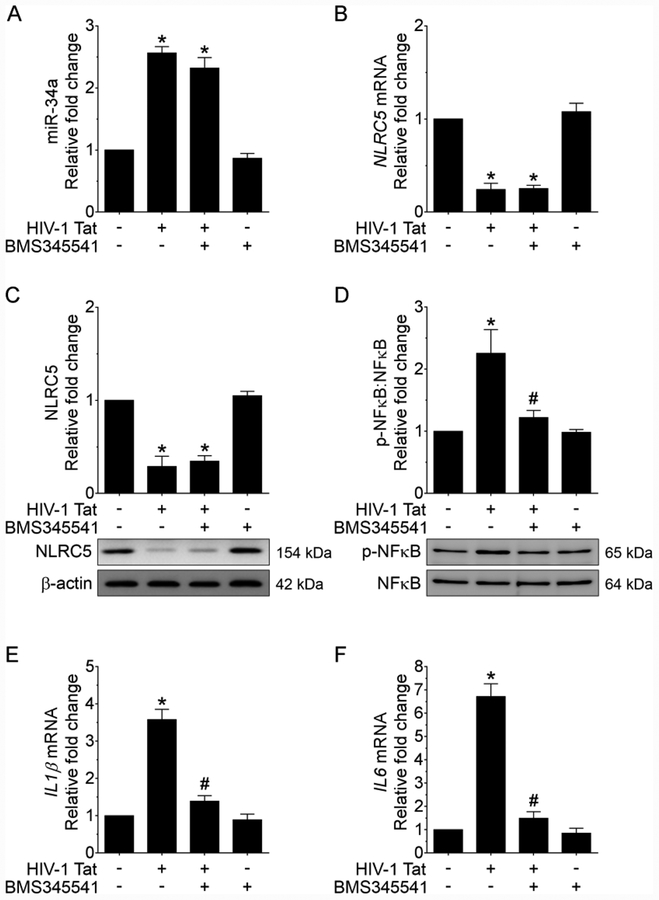
FIGURE 5.
Pharmacological inhibition of NFκB signaling alleviates HIV-1 Tat-mediated microglial inflammation. qPCR analysis showing expression of miRNA-34a (A) and NLRC5 mRNA (B) in mouse primary microglial cells pretreated with IKK complex inhibitor - BMS345541 for 1 h followed by exposure of cells to HIV-1 Tat (50 ng/ml; 24 h). Representative western blotting analysis showing expression levels of NLRC5 (C) and NFκB p65 (D) in mouse primary microglial cells pretreated with IKK complex inhibitor - BMS345541 (10 μM) for 1 h followed by exposure of cells to HIV-1 Tat (50 ng/ml; 24 h). qPCR analysis demonstrating mRNA expression of IL1β (E) and IL6 (F) in mouse primary microglial cells pretreated with IKK complex inhibitor - BMS345541 for 1 h followed by exposure of cells to HIV-1 Tat (50 ng/ml; 24 h). Data are mean±SEM of six independent experiments. β-Actin was probed as an internal control for all the experiments. Nonparametric Kruskal–Wallis one-way ANOVA followed by Dunn’s post hoc test was used to determine the statistical significance of multiple groups. *p < 0.05 versus control; #p < 0.05 versus HIV-1 Tat.