Figure 3.
Over-accumulation of HIF-1α Underlies Survival Defect and Distorted Metabolism in VHL-Deficient B Cells
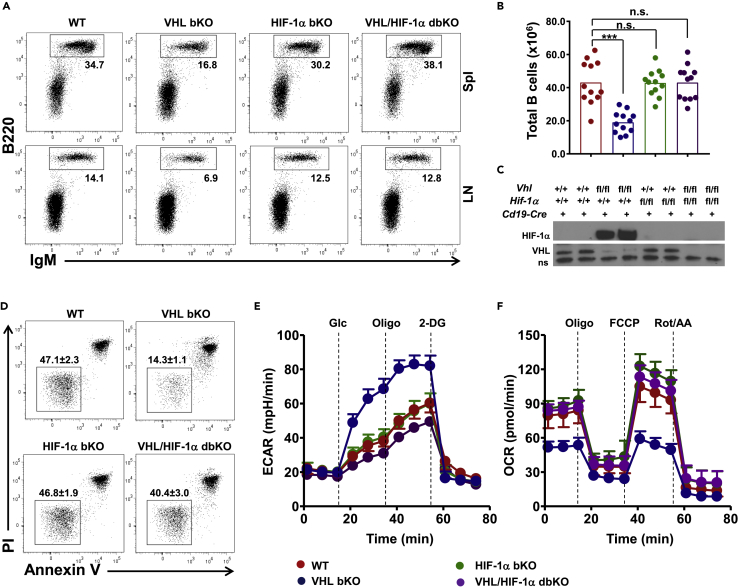
(A) Flow cytometric analysis of B cells in the spleen and lymph nodes of WT, VHL-deficient, HIF-1α bKO, and VHL/HIF-1α bdKO mice. Numbers adjacent to the outline areas indicate percentage of gated cells over total cells.
(B) Enumeration of total splenic B cells in mice of various genotypes. Each symbol represents one mouse, and the height of bars indicates the mean.
(C) Immunoblotting of HIF-1α and VHL in B cells of different genotypes as indicated. A non-specific (ns) band served as loading control.
(D) Flow cytometric analysis of the survival VHL/HIF-1α bdKO B cells. Splenic B cells were cultured in medium for 16 h and analyzed for Annexin V and propidium iodide (PI) staining. Numbers adjacent to outline areas indicate the percentage of PI−Annexin V− live B cells (mean ± SD, n = 5).
(E and F) ECAR and OCR analyses of B cells. ECAR (E) and OCR (F) of splenic B cells from mice of various genotypes were measured in real time with the addition of different compounds as indicated.
Data are representative of 12 (A), 3 (C), or 5 (D, E, and F) experiments. For E and F, each data point represents mean ± SD, n = 5. n.s., not significant; ***p < 0.001 (Student's t test). See also Figure S3.