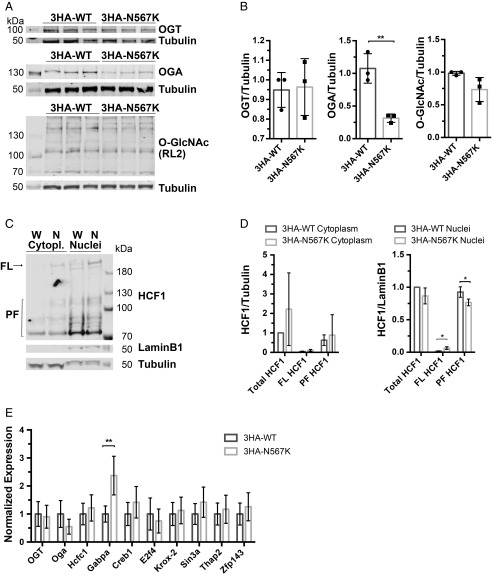
Fig. 4.
N567K mutation leads to defects in HCF1 processing and downstream gene expression in 3HA-OGTN567K pluripotent mESCs. (A) Immunoblots showing OGT, OGA, and protein O-GlcNAcylation (RL2) levels in 3HA-OGTWT and 3HA-OGTN567K undifferentiated mESCs. (B) Quantification of immunoblots of global protein O-GlcNAcylation, OGA, and OGT protein level in undifferentiated mESCs normalized to tubulin signal. n = 3, mean ± SD. Unpaired t test. **P = 0.0049. (C) 3HA-OGTN567K mESCs show impaired HCF1 proteolytic cleavage. Western blot analysis for HCF1, tubulin (cytoplasmic marker), and Laminin B1 (nuclear marker) indicates decreased level of proteolytic fragments of HCF1 in 3HA-OGTN567K compared with 3HA-OGTWT mESCs. (D) Quantification of immunoblots on nuclear and cytoplasmic fractions of undifferentiated 3HA-OGTN567K mESCs compared with 3HA-OGTWT mESCs control line showing HCF1 levels. HCF1 full-length (FL) and proteolytic fragments (PF) normalized to tubulin signal for the cytosolic fraction and to Lamin B1 signal for nuclear fraction. n = 3, mean ± SD. Multiple t test. *P = 0.0189 for FL and *P = 0.044 for PF. (E) qPCR analysis of gene expression of HCF1 targets in undifferentiated 3HA-OGTN567K and 3HA-OGTWT mESCs. Mean ± SEM, n = 3. **P = 0.002.