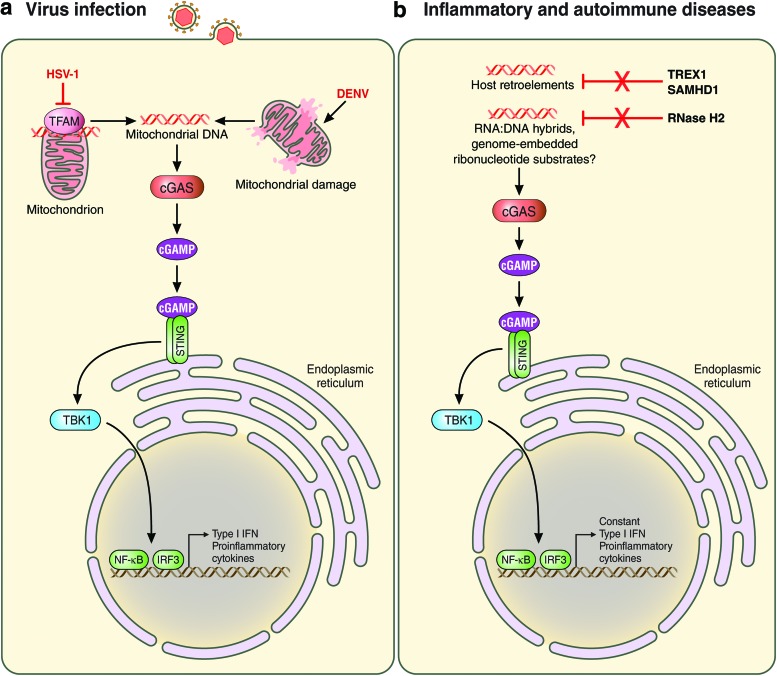
FIG. 2.
Endogenous DNA recognition by cGAS. Recognition of endogenous DNA species by cGAS during viral infection (a) or in inflammatory and autoimmune diseases (b). Following the recognition of cellular DNA, cGAS produces the second messenger cGAMP, which then binds to and activates STING at the ER. STING then recruits and activates the kinase TBK-1, leading to IRF3 activation. In addition, NF-κB is activated. The detailed mechanisms of host DNA recognition by cGAS are described in the text. Solid lines indicate direct effects or signaling events. Red lines indicate inhibitory events. cGAMP, cyclic GMP-AMP; cGAS, cyclic GMP-AMP synthase; DENV, dengue virus; ER, endoplasmic reticulum; STING, stimulator of IFN genes. Color images are available online.