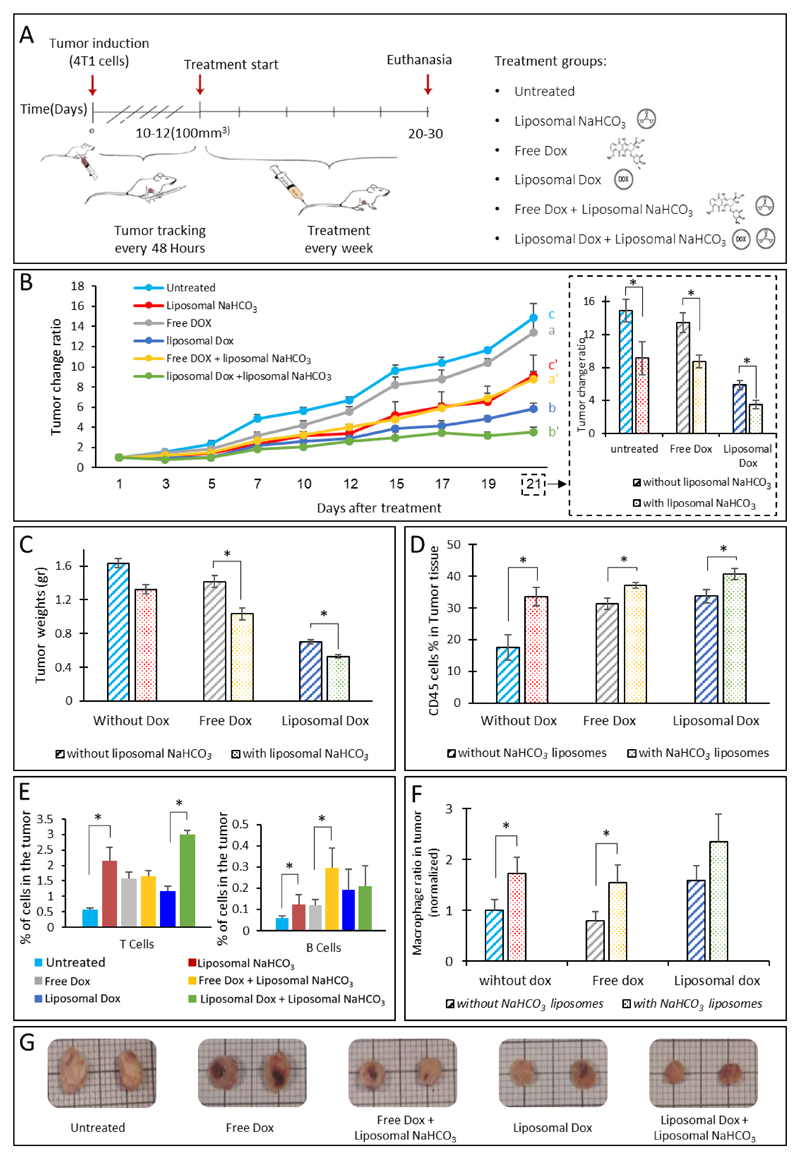
Figure 6.
Liposomal bicarbonate increases doxorubicin efficacy in breast cancer. The effect of liposomal bicarbonate as an adjuvant for enhancing doxorubicin activity in-vivo, was studied (A). Once tumors reached 100-200mm^3 treatments began, using free doxorubicin(dox) (4 mg/kg-body-weight), liposomal doxorubicin (4 mg/kg) and a combination of the two with liposomal NaHCO3. Tumors were sized every other day. In all the time points, for each mouse the tumor size was normalized to the initial size measured at day 1(B), a and a' show statistical differences(p<0.05) after 12 days and continued through the last time point (21 days), statistical differences(p<0.05) between b and b' were observed later, in the last two measurements. For c and c' differences were observed after 10 days (p<0.05). At the end of the experiments tumors were extracted, weighed and imaged (C and G). An increase in total immune cell (CD45+), T cells (CD3+), B cells (CD19+) and macrophages(CDF/48+) populations in the tumor tissue was also observed in the treatment groups (D-F). (F) Macrophages ratio in the tumor tissue normalized to untreated group. Error bars represent standard deviation of the mean from 4 to 5 independent repeats. *Significant difference between treatments, where *p<0.05, according to a Student’s t-test with a two-tailed distribution with equal variance.