Figure 4. Maternal Care Circuitry.
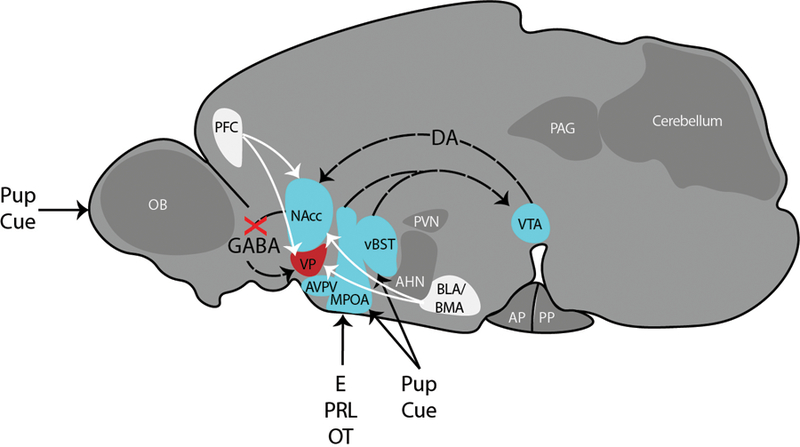
Circuit drawn in the sagittal orientation of a rodent brain based on our synthesis of [17,18,20]. Hormones of pregnancy restructure the MPOA, which along with the vBST receives inputs informing about offspring cues. The MPOA and vBST project to VTA, which in turn sends dopaminergic projections to the NAcc. In the maternal state, the GABAergic projections from the NAcc to the VP are inhibited, preventing avoidance and defense behaviors. The NAcc and VP also receive cues (white lines) of valence (both positive and negative) from the PFC and BLA-BMA. Maternal care is also supported by Tyrosine hydroxylase (TH)-expressing neurons in the AVPV. Abbreviations: AHN = anterior hypothalamic nucleus; AP = anterior pituitary; AVPV = anteroventral periventricular nucleus; BLA = basolateral amygdala; BMA = basomedial amygdala; DA = dopamine; E = estradiol; MeA = medial amygdala; MPOA = medial preoptic area; Nacc = nucleus accumbens; OB = olfactory bulb; OT = oxytocin; P = progesterone; PAG = periaqueductal gray; PFC = prefrontal cortex; PP = posterior pituitary; PRL = prolactin; PVN = paraventricular nucleus of the hypothalamus; SON = supraoptic nucleus of the hypothalamus; vBST = ventral bed nucleus of the stria terminalis; VP = ventral pallidum; VTA = ventral tegmental area
