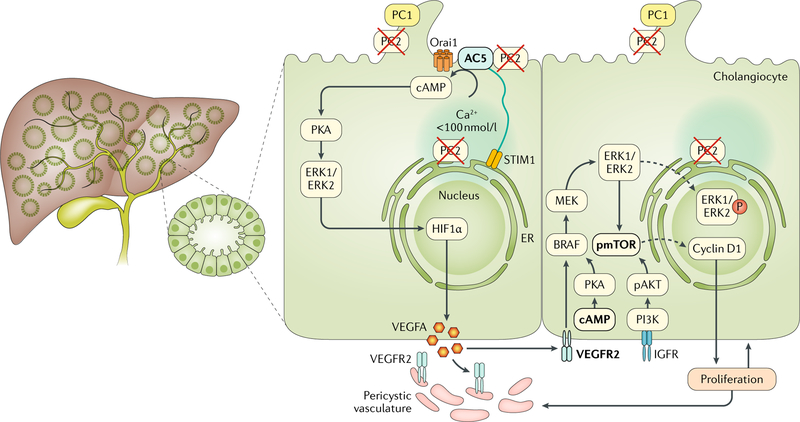
Fig. 2 |. Signalling mechanisms involved in cyst growth in ADPKD.
Autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease (ADPKD) is associated with mutations in one of two genes, PKD1 or PKD2, which encode polycystin-1 (PC1) and PC2, respectively. ADPKD is characterized by the presence of multiple cysts in the liver parenchyma that progressively dilate and grow. PC2-defective cholangiocytes are characterized by inappropriate production of cAMP and increased protein kinase A (PKA)-dependent activation of extracellular-signal-regulated kinase 1 (ERK1)/ERK2 and subsequently mechanistic target of rapamycin (mTOR), and hypoxia-inducible factor 1α (HIF1α)-increased production of cAMP is caused by changes in intracellular Ca2+ homeostasis. In PC2-defective cholangiocytes, store-operated Ca2+ entry is inhibited and cells respond to an acute reduction in endoplasmic reticulum (ER) Ca2+ levels with stromal interacting molecule 1 (STIM1)-dependent and adenylyl cyclase 5 (AC5)-dependent stimulation of cAMP production, which drives PKA-dependent activation of ERK1/ERK2. Defective PC2 also inhibits the interaction between STIM1 and Orai channels and maximizes the functional coupling of STIM1 to AC5, resulting in increased production of cAMP. PC2-defective cells respond to conditions that decrease ER Ca2+ levels and trigger oligomerization and membrane translocation of STIM1, with an overproduction of cAMP. In turn, cAMP activates the PKA–Ras–Raf–ERK pathway and stimulates vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) production through an mTOR–HIF1α-mediated mechanism. VEGF produced by cystic cholangiocytes increases perivascular microvascular density and cholangiocyte proliferation through binding with VEGF receptor 2 (VEGFR2). Stimulation of mTOR through AKT, for example, by insulin-like growth factor receptor (IGFR) ligand binding, can also activate ERK1/ERK2. Signalling molecules that are druggable are highlighted in bold and detailed in TABLE 2. PI3K, phosphoinositide 3-kinase; pmTOR, phosphorylated mTOR; pAKT, phosphorylated AKT.