Fig. 1.
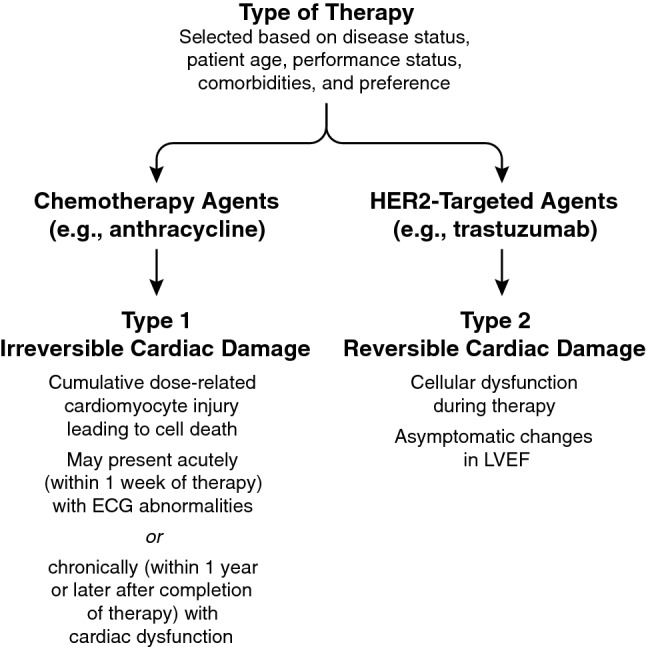
Schematic of Potential Mechanisms of Cardiotoxicity. There are 2 types of therapy selected based on disease status, patient age, performance status, comorbidities, and preference. Chemotherapy agents such as anthracycline can lead to irreversible (type 1) cardiac damage. With type 1 damage, cumulative dose-related cardiomyocyte injury leading to cell death can occur and may present acutely (within 1 week of therapy) with ECG abnormalities or chronically (within 1 year or later after completion of therapy) with cardiac dysfunction. HER2-targeted agents such as trastuzumab can lead to reversible (type 2) damage. With type 2 damage, cellular dysfunction during therapy and asymptomatic changes in LVEF can occur. ECG electrocardiogram, HER2 human epidermal growth factor receptor-2, LVEF left ventricular ejection fraction
