Figure 2.
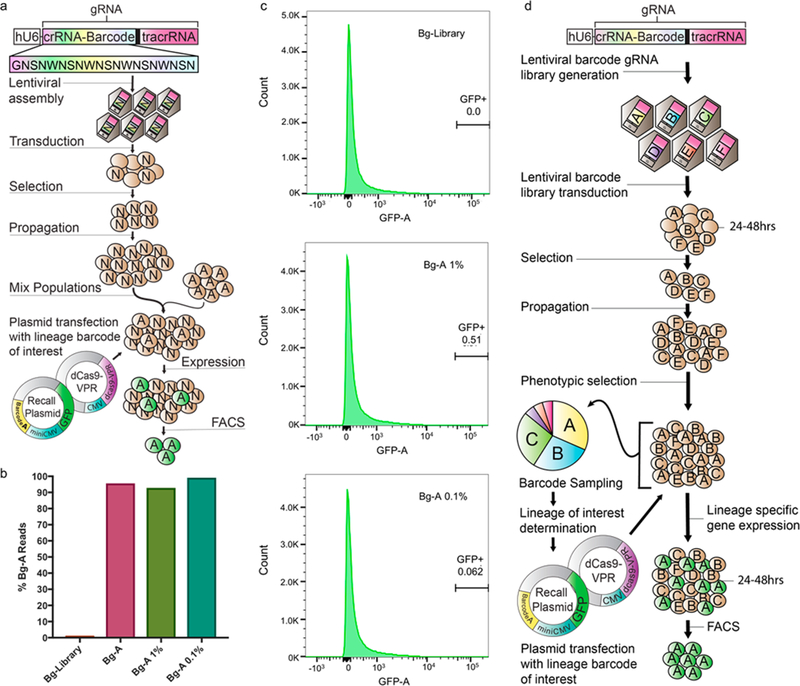
Isolation of a single lineage of interest within a high diversity population. (a) High diversity barcoded-gRNA HEK293T cell population was generated with a GNSNWNSNWNSNWNSNWNSN template. The HEK293T Bg-A population was spiked in with the high diversity Bg-Library population to obtain a 1% and 0.1% Bg-A mixed population. Bg-A cells were then isolated from the mixed population via cotransfection of the R-A_GFP plasmid and dCas9-VPR plasmid and cell sorted based off of GFP expression. (b) To initialize sorting gates and determine capture rate, the Bg-Library, Bg-A 1% and Bg-A 0.1% populations were transfected with the Recall components and flow analyzed. Sorting gates were set based off of the Bg-Library to have a 0% error-load, resulting in the capture of 0.51% and 0.062% of cells in the Bg-A 1% and Bg-A 0.1%, respectively. (c) Barcode sequencing of the Bg-library and Bg-A populations as well as the Bg-A 1% and 0.1% isolated populations. Barcode sequencing of the isolated Bg-A 1% and 0.1% population show 92.8% and 99.1% of the reads being Bg-A respectively, nearly identical to the 95.8% Bg-A reads from the sampled Bg-A population. (d) Example experimental workflow utilizing COLBERT. A population of cells are tagged with a library of expressed barcoded gRNAs. The barcoded population can subsequently go through a phenotypic selection of interest. The resulting selected population is then sampled for relative barcode abundance. The barcode analysis would inform lineages of interest and allow for lineage-specific Recall plasmids to be assembled and cotransfected with dCas9-VPR into the resultant population for lineage-specific gene expression. In this instance, GFP is expressed, allowing the lineage of interest to be cell sorted and isolated from the mixed population.
