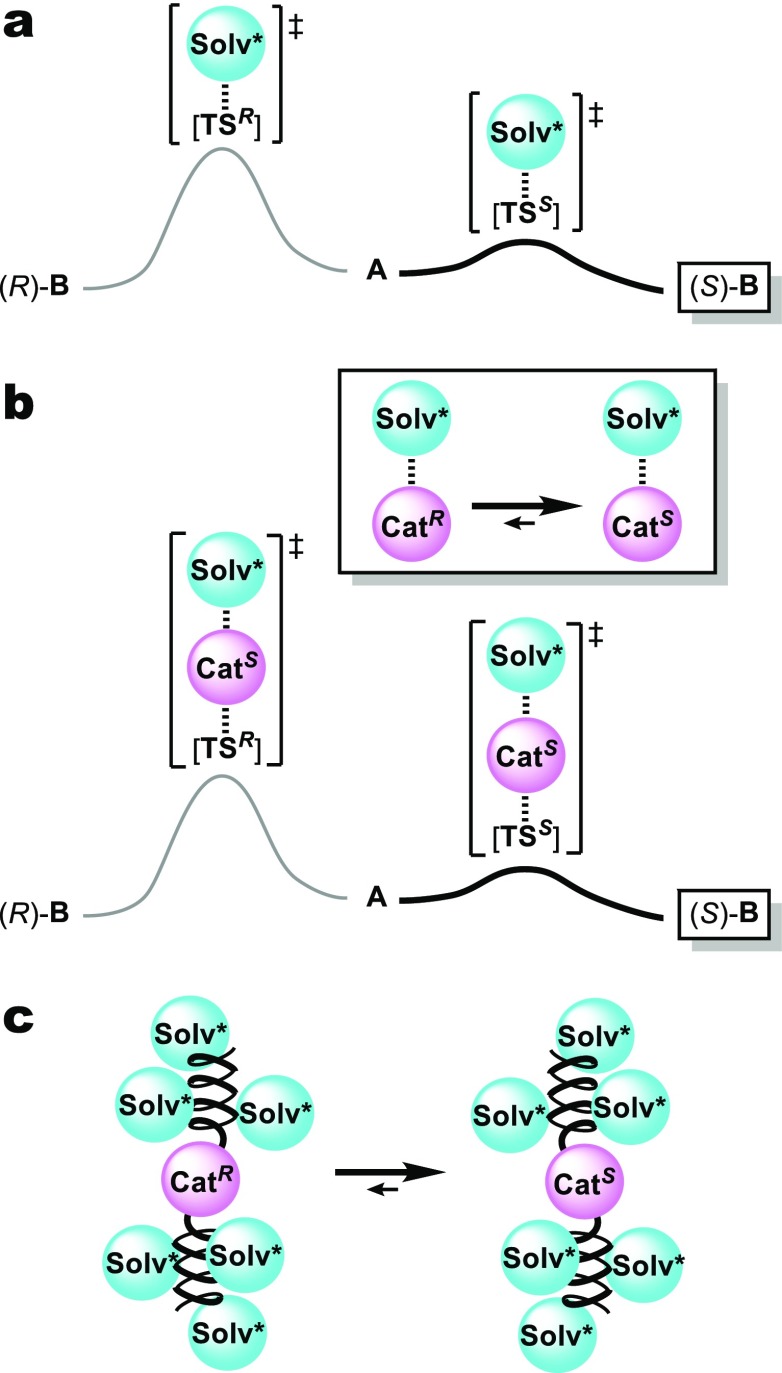
Figure 1.
Possible effect of chiral solvents on asymmetric reactions, in which the chiral solvent serves as the sole source of enantioselection. (a) Differentiation of two enantiomeric reaction pathways via the direct interaction between the chiral solvent (Solv*) with the transition structures (TSR and TSS). (b) The use of a catalyst with dynamic chirality, whose interactions with a chiral solvent induce one predominant enantiomeric chiral conformation (CatS). (c) Control of the dynamic chirality of a catalyst based on the induction of a chiral conformation in a helical macromolecule by a chiral solvent.