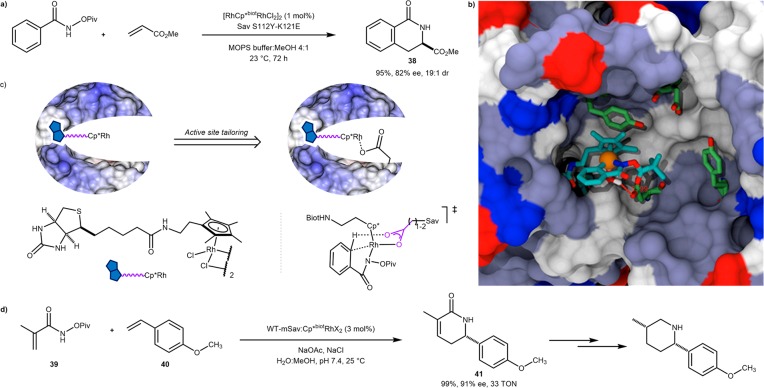
Scheme 19. Exploiting the CMD Mechanism for C–H Activation To Engineer an Artificial Benzannulase Based on the Biotin–Streptavidin Technology.
(a) Example of benzannulation resulting from iterative saturation mutagenesis. (b) Structure resulting from docking a computed cofactor in a partial X-ray structure. The positions of the rhodium and the nitrogen-amide were superimposed with the electron density from the X-ray structure. The protein is displayed as a solvent-accessible surface with mutated residues S112Y and K121E highlighted as green/red sticks. The cofactor is displayed as a stick and the rhodium as an orange sphere. (c) Cooperation from basic residue binding the active rhodium center. (d) Rovis’s benzannulation of representative hydroxamate ester 39 and styrene 40 by WT mSav:Cp*biotRhCl2 to afford δ-lactam 41.70