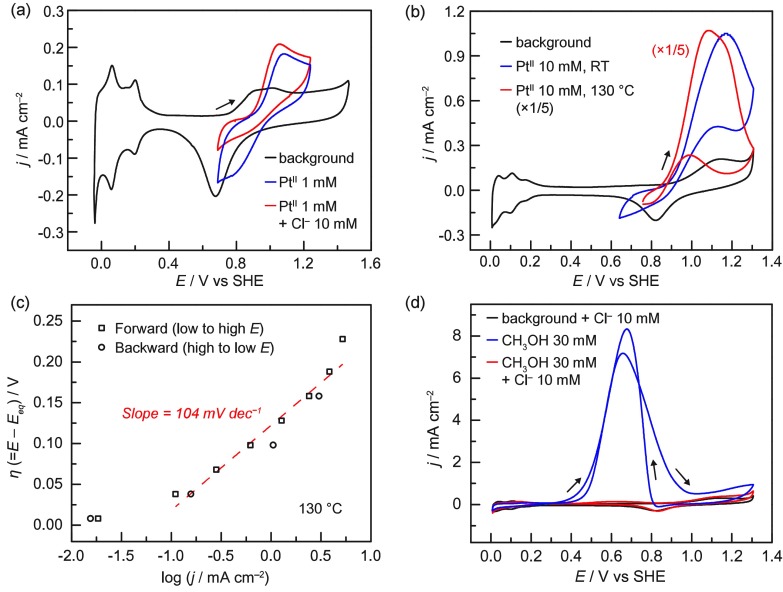
Figure 1.
(a) Cyclic voltammograms obtained on a Pt disk electrode at room temperature in 0.5 M H2SO4; (black) background, (blue) 1 mM K2PtIICl4, and (red) 1 mM K2PtIICl4 with 10 mM NaCl. (b) Cyclic voltammograms obtained on a Pt wire electrode in 10 mM NaCl, 0.5 M H2SO4; (black) background, (blue) 10 mM K2PtIICl4 at room temperature, and (red) 10 mM K2PtIICl4 at 130 °C. (c) Tafel plot at 130 °C for PtII electro-oxidation. The solution contained 5 mM each of K2PtIICl4 and Na2PtIVCl6 in 10 mM NaCl, 0.5 M H2SO4. Eeq (= 0.829 V vs SHE) was obtained from the open-circuit potential. (d) Cyclic voltammograms obtained on a Pt wire electrode in 10 mM NaCl, 0.5 M H2SO4 at 130 °C; (black) background, (blue) 30 mM CH3OH without the 10 mM NaCl, and (red) 30 mM CH3OH. All scan rates = 100 mV s–1.