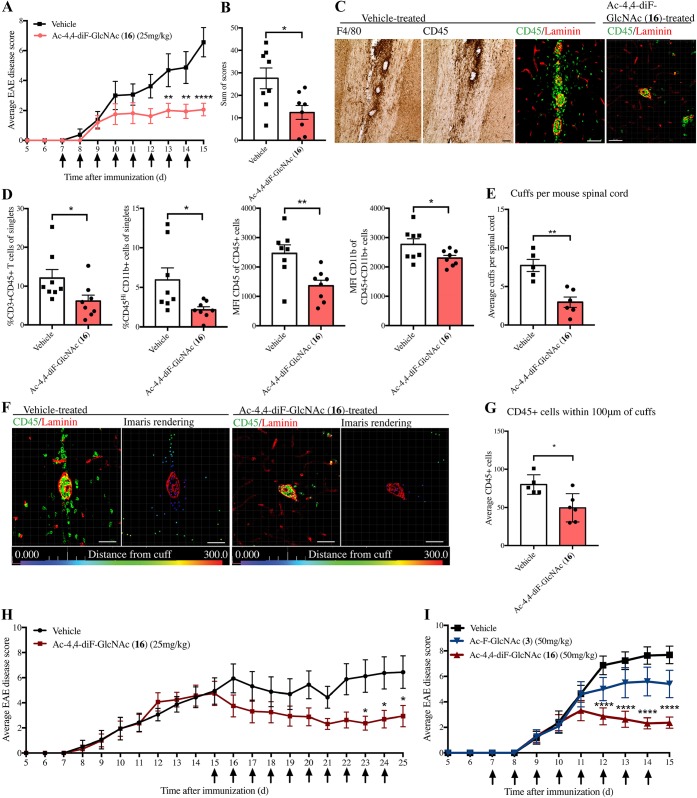
Figure 5.
Ac-4,4-diF-GlcNAc 16 attenuates EAE. (A) Average daily EAE clinical score of mice treated daily with 25 mg/kg Ac-4,4-diF-GlcNAc 16 or saline vehicle (N = 8) with treatment shown by arrows; mice are analyzed in parts C to G. (B) Sum of scores displaying individual burden of disease. (C) Brightfield images of F4/80 and CD45 and immunofluorescence of CD45 and laminin in vehicle- or Ac-4,4-diF-GlcNAc (16)-treated mice (scale bar 50 μm). (D) Flow cytometry of the spinal cord showing Ac-4,4-diF-GlcNAc 16 treatment reduces %CD3+ T cells and %CD45HiCD11b+ monocytes/macrophages (and median fluorescence intensity). (E) Average perivascular cuffs per spinal cord per mouse in treated and vehicle-treated EAE mice. (F) Immunohistochemistry of perivascular cuffs next to the Imaris-processed image (bar = 50 μm). (G) Number of CD45+ cells within 100 μm of perivascular cuffs, quantified by Imaris. (H) Average daily EAE clinical score of mice treated with 25 mg/kg Ac-4,4-diF-GlcNAc or vehicle from peak clinical severity (N = 8). (I) Average daily EAE clinical score of EAE mice treated with 50 mg/kg Ac-4,4-diF-GlcNAc 16, Ac-4-F-GlcNAc 3, or vehicle from preonset (N = 10); arrows indicate daily injections. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ****P < 0.0001. EAE scores (parts A, H, and I) were analyzed by two-way repeated-measures ANOVA with Sidak’s post hoc test versus vehicle; mean ± s.e.m. Parts B, D, E, and G were analyzed by two-tailed unpaired t test; mean ± s.d.