Fig. 4.
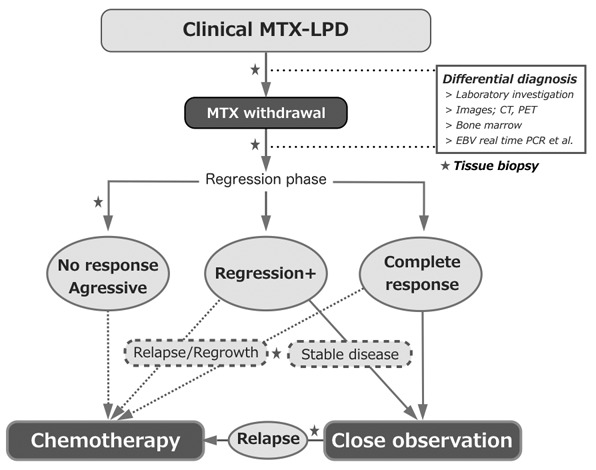
Clinical management of methotrexate-associated lymphoproliferative disorders (MTX-LPD)
When clinical-MTX-LPD develops, MTX withdrawal is the first procedure. In addition to watchful waiting, the differential diagnosis is performed by laboratory investigation and imaging. Bone marrow aspiration/biopsy and the measurement of EBV viral load are considered according to the patient’s clinicopathogenesis. To diagnose LPD, tissue biopsy is required at any time during the clinical course. After MTX withdrawal, chemotherapy is considered for patients with non-regressive LPD or aggressive LPD, and relapse/regrowth after the regressive phase. Among patients with residual LPD under LPD regression, the decision for chemotherapy is based on the physician’s assessment.
