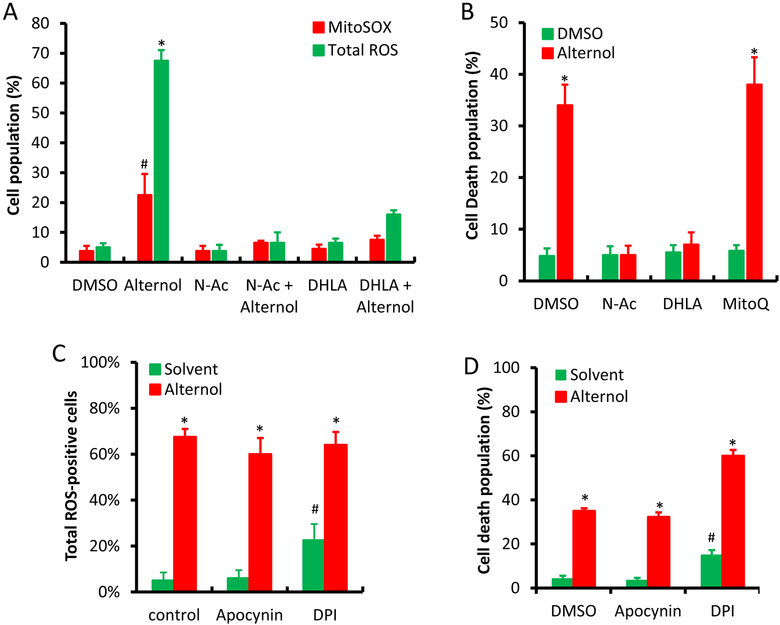
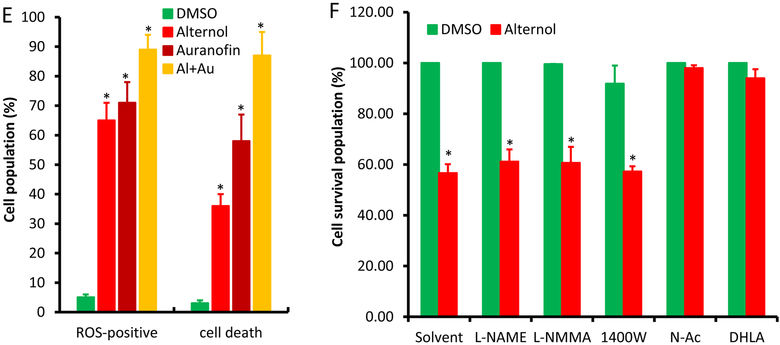
Fig 1.
Mitochondrial superoxide, NOX and NOS are not involved in Alternol-induced ROS-dependent cell death in PC-3 cells. A & C; PC-3 cells were seeded in 24-well pallets overnight and then loaded with MitoSOX (5 μM) or total ROS fluorescent probe for 30 min. After media replacement, cells were treated with Alternol plus or minus ROS scavengers (N-Ac 5 mM, DHLA 0.25 mM) or NOX inhibitors (DPI 10 μM and Apocynin 1 μM) for 4 h. Fluorescent positive cells with MitoSOX or total ROS probe were counted under fluorescent microscope as described [22].
B & D; PC-3 cells seeded in 24-well plates were treated with Alternol plus or minus N-Ac (5 mM), DHLA (0.25 mM) or MitoQ (5 μM) for 8 h. Cell death rate was determined using trypan blue exclusion assay as described [22].
E; PC-3 cells seeded in 24-well plates were loaded with total ROS fluorescent probe for 30 min and then treated with Alternol (10 μM) or Auranofin (5 μM) as indicated for 8 h. Cell populations for total ROS-positive or dying cells were determined as described above [22].
F; PC-3 cells seeded in 24-well plates were treated with Alternol (10 μM) plus or minus NOS inhibitors (L-NAME 10 μM, L-NMMA 10 μM, 1400W 1 μM) for 8 h. Cell survival rate was determined using SRB assay as described [24].
All experiments were reaped in triplicates and the data were presented as MEAN. The error bar represents the SEM of the MEAN. A statistical significance (Student t-test) was indicated with the asterisk (p < 0.01) or the hashtag (p < 0.05) compared to the solvent/DMSO control.